K8s-client-go(Informer机制)
K8s-client-go(Informer机制)
基于1.25
什么是Informer
Informer实现了组件之间使用HTTP通信,但是不依赖任何中间件的情况下,实现了保证消息的实时性、可靠性、顺序性等
使用示例
package main |
首先通过kubernetes.NewForConfig func创建clientSet对象,Informer需要通过ClientSet与kube-apiserver进行交互
Informer是一个持久运行的协程
Informer架构
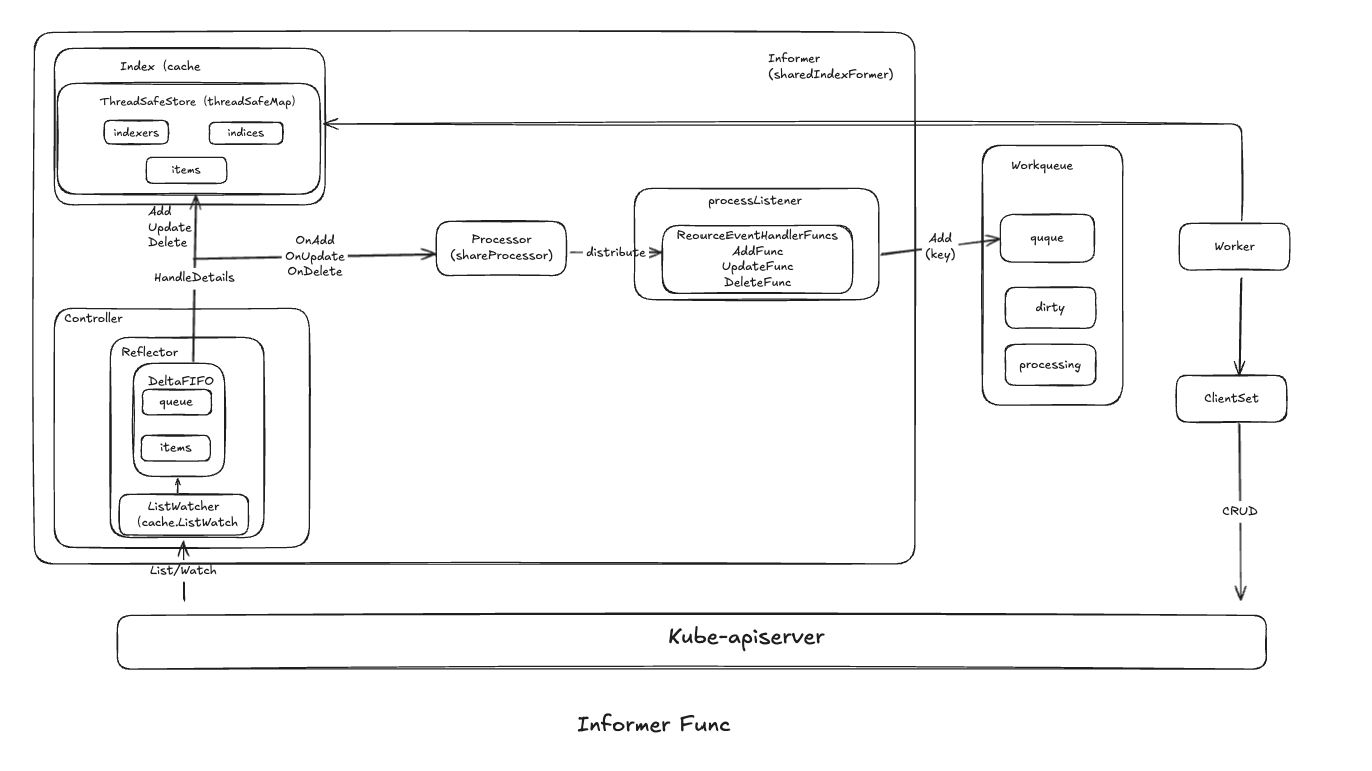
Relector
Relector用于监听指定的资源,监听资源发生变化,触发对应的变更事件:Added、Updated、Deleted事件,并且把对应的操作缓存到DeltaFIFO中
DeltaFIFO有俩部分:
- Delta:资源对象的存储,保存资源的操作类型:Added、Updated、Deleted事件
- FIFO:先进先出的队列,有队列的基础方法
Controller
Controller是Relector的控制器,根据配置信息,构建管理Relector对象
- 周期性处理DeltaFIFO中的数据,驱动数据向下链路分发
Indexer
Indexer是client-go中一个核心组件,负责在客户端缓存和索引K8s资源,提供高效的对象查询和访问机制
- 在客户端内存中维护了K8s资源对象的缓存,减少对kube-apiserver的请求次数
- 允许K8s资源定义索引,实现基于索引的快速检索
processor
processor注册了一系列的监听器,获取从DeltaFIFO中分发的资源对象,并把这些资源对象分发给注册的每个监听器
- process在分发资源对象的时候,会特别识别Sync事件,并把这个事件分发给等待同步事件的监听器
processorListener
processorListener为Informer适用方提供定制行为的扩展能力
- 使用ResourceEventHandler定义感知资源对象的Added、Updated、Deleted
- 根据收到的processor的事件,做OnAdd、OnUpdate、OnDelete
workqueue和Worker
workqueue是工作队列,它支持了多个生产者和消费者按照顺序处理,并且保证相同元素在同一事件不会被重复处理
- K8s许多控制器在接受到对应的资源对象更变,会使用workqueue把对应的资源对象key存入workqueue,并且启动独立的goroutime获取队列中的数据
Reflector数据同步
Reflector是Informer与kube-apiserver通信的桥梁,它监听指定的资源,在发现资源对象和对应的变更信息,把这些资源对象同步到本地缓存DeltaFIFO中
- Informer启动的时候,使用NewReflector func实例化Reflector对象,实例化需要传入ListWatcher对象,拥有List和Watch func
获取资源列表
ListAndWatch使用list func在首次启动或有wait.BackoffUnitl重新拉起获取资源下所有的对象的数据并其存储至DeltaFIFO
list如下:
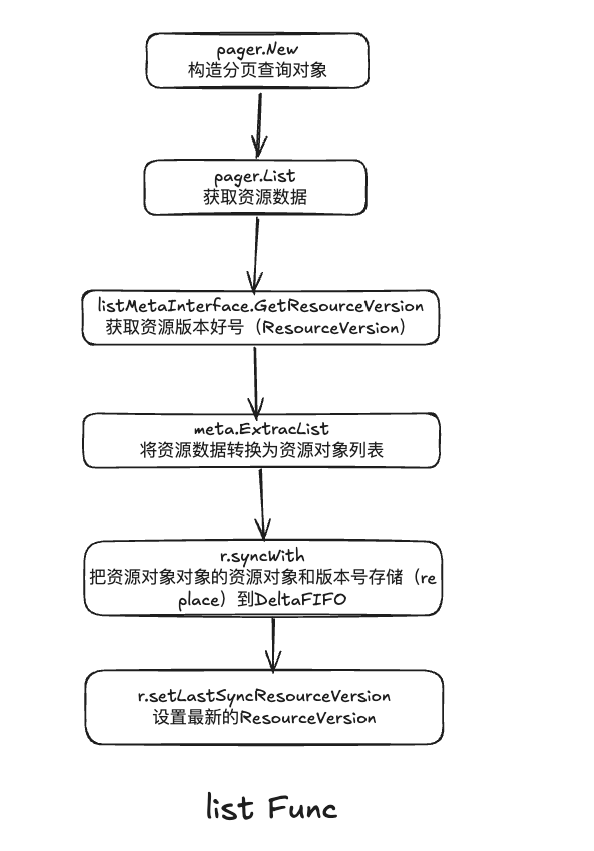
- pager.New func构造出查询列表的分页数据对象ListPager
- ListPager是Client-go中的工具类,采用分页的形式,使用用户自定义的页距查询函数(默认查询分页大小500)
- pager.List用于获取资源的所有对象数据
- 优先采用多批次的分页数据
- 如果分页查询失败,采用降级全量查询,通过options的ResourceVersion字段控制(为0代表获取所有Pod)
- pager.List有点类似于端点续传,因为网络原因端开依旧能实现继续传输
- listMetaInterface.GetResourceVersion用于获取ResourceVersion
- ResourceVersion是标识符,kube-apiserver每次更新都会更新ResourceVersion
- meta.ExtracList用于把资源数据转换为资源对象列表,将runntime.Object对象转换为[]runntime.Object列表
- r.syncWith用于把资源对象列表中的资源对象和Resource Version存储到DeltaFIFO,并且替换已经存在的资源对象
- r.setLastSyncResourceVersion用于设置最新的ResourceVersion
// list simply lists all items and records a resource version obtained from the server at the moment of the call. |
监听资源对象
Watch操作会与kube-apiserver简历长链接(支持HTTP/1.1 chunked、WebSocket、HTTP/2(优先选择),接受kube-apiserver发送过来的资源变更事件
当使用HTTP/2 Watch操作使用Frame进行传输,类似很多RPC协议
Frame使用二进制编码,通过帧头固定位置的字节描述Body长度就可以读取Body,知道Flag遇到END_STREAM
-
options := metav1.ListOptions{
ResourceVersion: r.LastSyncResourceVersion(),
// We want to avoid situations of hanging watchers. Stop any watchers that do not
// receive any events within the timeout window.
TimeoutSeconds: &timeoutSeconds,
// To reduce load on kube-apiserver on watch restarts, you may enable watch bookmarks.
// Reflector doesn't assume bookmarks are returned at all (if the server do not support
// watch bookmarks, it will ignore this field).
AllowWatchBookmarks: true,
}
// start the clock before sending the request, since some proxies won't flush headers until after the first watch event is sent
start := r.clock.Now()
w, err := r.listerWatcher.Watch(options)
if err != nil {
// If this is "connection refused" error, it means that most likely apiserver is not responsive.
// It doesn't make sense to re-list all objects because most likely we will be able to restart
// watch where we ended.
// If that's the case begin exponentially backing off and resend watch request.
// Do the same for "429" errors.
if utilnet.IsConnectionRefused(err) || apierrors.IsTooManyRequests(err) {
<-r.initConnBackoffManager.Backoff().C()
continue
}
return err
}
err = watchHandler(start, w, r.store, r.expectedType, r.expectedGVK, r.name, r.expectedTypeName, r.setLastSyncResourceVersion, r.clock, resyncerrc, stopCh)
retry.After(err)
if err != nil {
if err != errorStopRequested {
switch {
case isExpiredError(err):
// Don't set LastSyncResourceVersionUnavailable - LIST call with ResourceVersion=RV already
// has a semantic that it returns data at least as fresh as provided RV.
// So first try to LIST with setting RV to resource version of last observed object.
klog.V(4).Infof("%s: watch of %v closed with: %v", r.name, r.expectedTypeName, err)
case apierrors.IsTooManyRequests(err):
klog.V(2).Infof("%s: watch of %v returned 429 - backing off", r.name, r.expectedTypeName)
<-r.initConnBackoffManager.Backoff().C()
continue
case apierrors.IsInternalError(err) && retry.ShouldRetry():
klog.V(2).Infof("%s: retrying watch of %v internal error: %v", r.name, r.expectedTypeName, err)
continue
default:
klog.Warningf("%s: watch of %v ended with: %v", r.name, r.expectedTypeName, err)
}
}
return nil
WatchHandler func处理资源对象的变更事件,触发Addded、Updated、Deleted事件,把对应的资源对象更新到本地缓存DeltaFIFO中并且更新ResourceVersion
-
// watchHandler watches w and sets setLastSyncResourceVersion
func watchHandler(start time.Time,
w watch.Interface,
store Store,
expectedType reflect.Type,
expectedGVK *schema.GroupVersionKind,
name string,
expectedTypeName string,
setLastSyncResourceVersion func(string),
clock clock.Clock,
errc chan error,
stopCh <-chan struct{},
) error {
eventCount := 0
// Stopping the watcher should be idempotent and if we return from this function there's no way
// we're coming back in with the same watch interface.
defer w.Stop()
loop:
for {
select {
case <-stopCh:
return errorStopRequested
case err := <-errc:
return err
case event, ok := <-w.ResultChan():
if !ok {
break loop
}
if event.Type == watch.Error {
return apierrors.FromObject(event.Object)
}
if expectedType != nil {
if e, a := expectedType, reflect.TypeOf(event.Object); e != a {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: expected type %v, but watch event object had type %v", name, e, a))
continue
}
}
if expectedGVK != nil {
if e, a := *expectedGVK, event.Object.GetObjectKind().GroupVersionKind(); e != a {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: expected gvk %v, but watch event object had gvk %v", name, e, a))
continue
}
}
meta, err := meta.Accessor(event.Object)
if err != nil {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: unable to understand watch event %#v", name, event))
continue
}
resourceVersion := meta.GetResourceVersion()
switch event.Type {
case watch.Added:
err := store.Add(event.Object)
if err != nil {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: unable to add watch event object (%#v) to store: %v", name, event.Object, err))
}
case watch.Modified:
err := store.Update(event.Object)
if err != nil {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: unable to update watch event object (%#v) to store: %v", name, event.Object, err))
}
case watch.Deleted:
// TODO: Will any consumers need access to the "last known
// state", which is passed in event.Object? If so, may need
// to change this.
err := store.Delete(event.Object)
if err != nil {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: unable to delete watch event object (%#v) from store: %v", name, event.Object, err))
}
case watch.Bookmark:
// A `Bookmark` means watch has synced here, just update the resourceVersion
default:
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: unable to understand watch event %#v", name, event))
}
setLastSyncResourceVersion(resourceVersion)
if rvu, ok := store.(ResourceVersionUpdater); ok {
rvu.UpdateResourceVersion(resourceVersion)
}
eventCount++
}
}
watchDuration := clock.Since(start)
if watchDuration < 1*time.Second && eventCount == 0 {
return fmt.Errorf("very short watch: %s: Unexpected watch close - watch lasted less than a second and no items received", name)
}
klog.V(4).Infof("%s: Watch close - %v total %v items received", name, expectedTypeName, eventCount)
return nil
}
定期同步机制
ListAndWatch func启动了一个独立的groutime,用于定时把底层中的资源对象同步到DeltaFIFO中,同步的时间周期为创建Reflector时指定的resyncPeroid
go func() { |
-
func (f *DeltaFIFO) syncKeyLocked(key string) error {
// f.knownObjects是Indexer底层存储对象
obj, exists, err := f.knownObjects.GetByKey(key)
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf("Unexpected error %v during lookup of key %v, unable to queue object for sync", err, key)
return nil
} else if !exists {
klog.Infof("Key %v does not exist in known objects store, unable to queue object for sync", key)
return nil
}
// If we are doing Resync() and there is already an event queued for that object,
// we ignore the Resync for it. This is to avoid the race, in which the resync
// comes with the previous value of object (since queueing an event for the object
// doesn't trigger changing the underlying store <knownObjects>.
id, err := f.KeyOf(obj)
if err != nil {
return KeyError{obj, err}
}
if len(f.items[id]) > 0 {
return nil
}
// 把资源对象的同步操作写入DeltaFIFO
if err := f.queueActionLocked(Sync, obj); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("couldn't queue object: %v", err)
}
return nil
}
DeltaFIFO
DeltaFIFO队列和普通队列不一样的,不是存储资源对象本身,而是存储资源对象相关的操作记录
-
// DeltaFIFO is like FIFO, but differs in two ways. One is that the
// accumulator associated with a given object's key is not that object
// but rather a Deltas, which is a slice of Delta values for that
// object. Applying an object to a Deltas means to append a Delta
// except when the potentially appended Delta is a Deleted and the
// Deltas already ends with a Deleted. In that case the Deltas does
// not grow, although the terminal Deleted will be replaced by the new
// Deleted if the older Deleted's object is a
// DeletedFinalStateUnknown.
//
// The other difference is that DeltaFIFO has two additional ways that
// an object can be applied to an accumulator: Replaced and Sync.
// If EmitDeltaTypeReplaced is not set to true, Sync will be used in
// replace events for backwards compatibility. Sync is used for periodic
// resync events.
//
// DeltaFIFO is a producer-consumer queue, where a Reflector is
// intended to be the producer, and the consumer is whatever calls
// the Pop() method.
//
// DeltaFIFO solves this use case:
// - You want to process every object change (delta) at most once.
// - When you process an object, you want to see everything
// that's happened to it since you last processed it.
// - You want to process the deletion of some of the objects.
// - You might want to periodically reprocess objects.
//
// DeltaFIFO's Pop(), Get(), and GetByKey() methods return
// interface{} to satisfy the Store/Queue interfaces, but they
// will always return an object of type Deltas. List() returns
// the newest object from each accumulator in the FIFO.
//
// A DeltaFIFO's knownObjects KeyListerGetter provides the abilities
// to list Store keys and to get objects by Store key. The objects in
// question are called "known objects" and this set of objects
// modifies the behavior of the Delete, Replace, and Resync methods
// (each in a different way).
//
// A note on threading: If you call Pop() in parallel from multiple
// threads, you could end up with multiple threads processing slightly
// different versions of the same object.
type DeltaFIFO struct {
// lock/cond protects access to 'items' and 'queue'.
lock sync.RWMutex
cond sync.Cond
// `items` maps a key to a Deltas.
// Each such Deltas has at least one Delta.
items map[string]Deltas
// `queue` maintains FIFO order of keys for consumption in Pop().
// There are no duplicates in `queue`.
// A key is in `queue` if and only if it is in `items`.
queue []string
// populated is true if the first batch of items inserted by Replace() has been populated
// or Delete/Add/Update/AddIfNotPresent was called first.
populated bool
// initialPopulationCount is the number of items inserted by the first call of Replace()
initialPopulationCount int
// keyFunc is used to make the key used for queued item
// insertion and retrieval, and should be deterministic.
keyFunc KeyFunc
// knownObjects list keys that are "known" --- affecting Delete(),
// Replace(), and Resync()
knownObjects KeyListerGetter
// Used to indicate a queue is closed so a control loop can exit when a queue is empty.
// Currently, not used to gate any of CRUD operations.
closed bool
// emitDeltaTypeReplaced is whether to emit the Replaced or Sync
// DeltaType when Replace() is called (to preserve backwards compat).
emitDeltaTypeReplaced bool
// Called with every object if non-nil.
transformer TransformFunc
}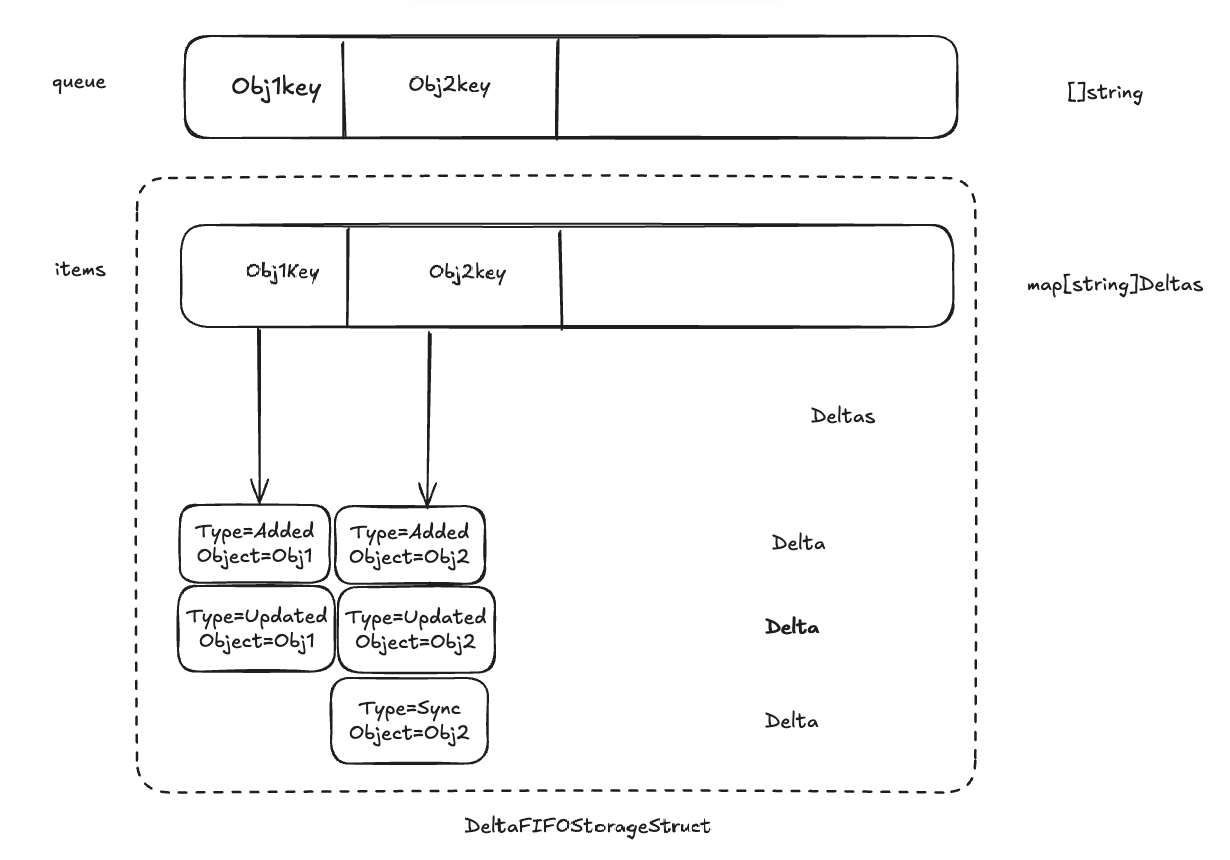
quque字段存储资源对象的key,key通过KeyOf func计算得到
items字段通过map存储,value是操作记录的切片
生产者方法
// queueActionLocked appends to the delta list for the object. |
消费者方法
Pop作为消费者方法,从DeltaFIFO的头部取出最早进入queue的数据
|
Contoller使用processLoop从DeltaFIFO去除数据给process,process具体使用
-
// Multiplexes updates in the form of a list of Deltas into a Store, and informs
// a given handler of events OnUpdate, OnAdd, OnDelete
func processDeltas(
// Object which receives event notifications from the given deltas
handler ResourceEventHandler,
clientState Store,
deltas Deltas,
isInInitialList bool,
) error {
// from oldest to newest
for _, d := range deltas {
obj := d.Object
switch d.Type {
case Sync, Replaced, Added, Updated:
// 判断资源是否存在
// 如果存在,就把资源添加到Indexer
// 不存在,就从Indexer删除
if old, exists, err := clientState.Get(obj); err == nil && exists {
if err := clientState.Update(obj); err != nil {
return err
}
handler.OnUpdate(old, obj)
} else {
if err := clientState.Add(obj); err != nil {
return err
}
handler.OnAdd(obj, isInInitialList)
}
case Deleted:
// 如果是删除,之间删除对象从Indexder
if err := clientState.Delete(obj); err != nil {
return err
}
handler.OnDelete(obj)
}
}
return nil
}
Indexer资源缓存
Indexer是client-go中存储资源对象并且自带索引的本地存储功能
ThreadSafeMap并发安全存储
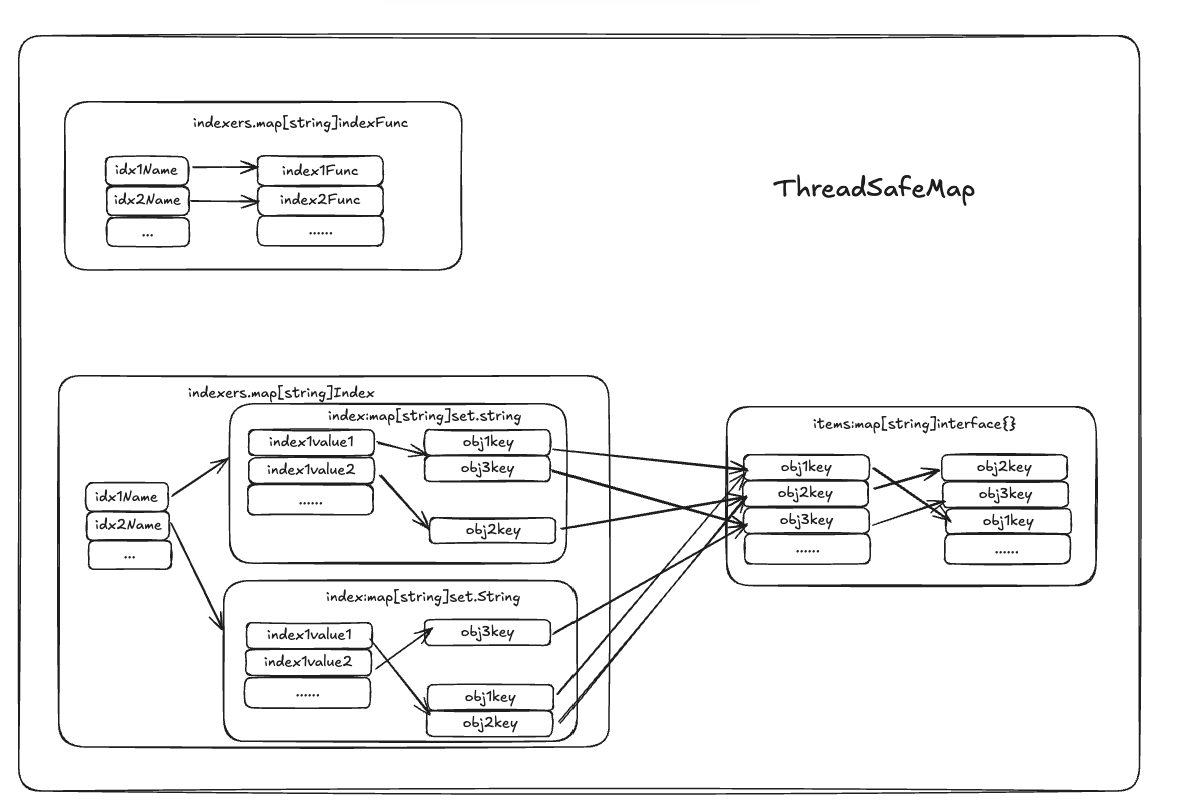
ThreadSafeMap是一个内存中的存储,它实现了资源数据的并发安全存储。
- 拥有Add、Updtae、Delete、List、Get、Replace、Resync等操作,还有索引函数(Indexers)和索引表(Indices)
- items是存储的资源对象,其中items的key通过keyFunc 计算得到,默认使用MetaNamespaceKeyFunc实现,计算得出格式为
/ 格式 - indexers是一个map数据结构,其中,key为用于检索资源对象的索引名称,value为该索引对应的索引函数
- indices是一个俩层的map数据结构,里面保存了每个索引经过索引函数得到的索引值,以及该索引值匹配的所有资源对象主键(objkey)列表
- lock读写锁控制,并发的安全访问
-
// threadSafeMap implements ThreadSafeStore
type threadSafeMap struct {
lock sync.RWMutex
items map[string]interface{}
// indexers maps a name to an IndexFunc
indexers Indexers
// indices maps a name to an Index
indices Indices
}
Indxder对象资源索引器
在ThreadSafeMap实现了封装,继承了ThreadSafeMap相关操作方法
-
// Indexer extends Store with multiple indices and restricts each
// accumulator to simply hold the current object (and be empty after
// Delete).
//
// There are three kinds of strings here:
// 1. a storage key, as defined in the Store interface,
// 2. a name of an index, and
// 3. an "indexed value", which is produced by an IndexFunc and
// can be a field value or any other string computed from the object.
type Indexer interface {
//ThreadSafeMap抽象定义,提供访问ThreadSafeMap中缓存数据和索引数据的方法
Store
// Index returns the stored objects whose set of indexed values
// intersects the set of indexed values of the given object, for
// the named index
// 根据指定的索引名称和示例对象,返回索引名称对象的索引值的所有资源对象列表
Index(indexName string, obj interface{}) ([]interface{}, error)
// IndexKeys returns the storage keys of the stored objects whose
// set of indexed values for the named index includes the given
// indexed value
// 给定索引名称和索引值,查询满足条件的所有资源对象主键列表
IndexKeys(indexName, indexedValue string) ([]string, error)
// ListIndexFuncValues returns all the indexed values of the given index
// 根据指定索引名称返回所有的索引值和名称
ListIndexFuncValues(indexName string) []string
// ByIndex returns the stored objects whose set of indexed values
// for the named index includes the given indexed value
// 给定索引名称如索引值,查询满足条件的资源对象列表
ByIndex(indexName, indexedValue string) ([]interface{}, error)
// GetIndexers return the indexers
// 返回所有索引对象
GetIndexers() Indexers
// AddIndexers adds more indexers to this store. If you call this after you already have data
// in the store, the results are undefined.
// 在填充ThreadSafeMap中的缓存资源对象前添加更多的索引对象
AddIndexers(newIndexers Indexers) error
}
使用示例
package main |
process资源处理
从DeltaFIFO获得的资源操作记录,在交由Indexer存储在本地缓存,还会推送到processor
- processor是资源对象操作记录的处理器,分发到不同的监听器中
监听器的注册和管理
-
// sharedProcessor has a collection of processorListener and can
// distribute a notification object to its listeners. There are two
// kinds of distribute operations. The sync distributions go to a
// subset of the listeners that (a) is recomputed in the occasional
// calls to shouldResync and (b) every listener is initially put in.
// The non-sync distributions go to every listener.
type sharedProcessor struct {
listenersStarted bool
listenersLock sync.RWMutex
listeners []*processorListener
syncingListeners []*processorListener
clock clock.Clock
wg wait.Group
}listeners为注册到processor的监听器
syncingListeners为所有进入同步周期的监听器
监听器默认会被同事添加到这俩个监听器列表中
每一个listener监听器都说一个processorListener对象
Informer机制使用方可以使用AddEventHandler func或AddEventHandlerWithResyncPeriod func把新的监听器注册到processor中
- AddEventHandler 在添加监听器会使用Refector的同步周期作为监听器的同步周期
- AddEventHandlerWithResyncPeriod func作为监听器专属的同步周期
-
func (s *sharedIndexInformer) AddEventHandlerWithResyncPeriod(handler ResourceEventHandler, resyncPeriod time.Duration) {
s.startedLock.Lock()
defer s.startedLock.Unlock()
if s.stopped {
klog.V(2).Infof("Handler %v was not added to shared informer because it has stopped already", handler)
return
}
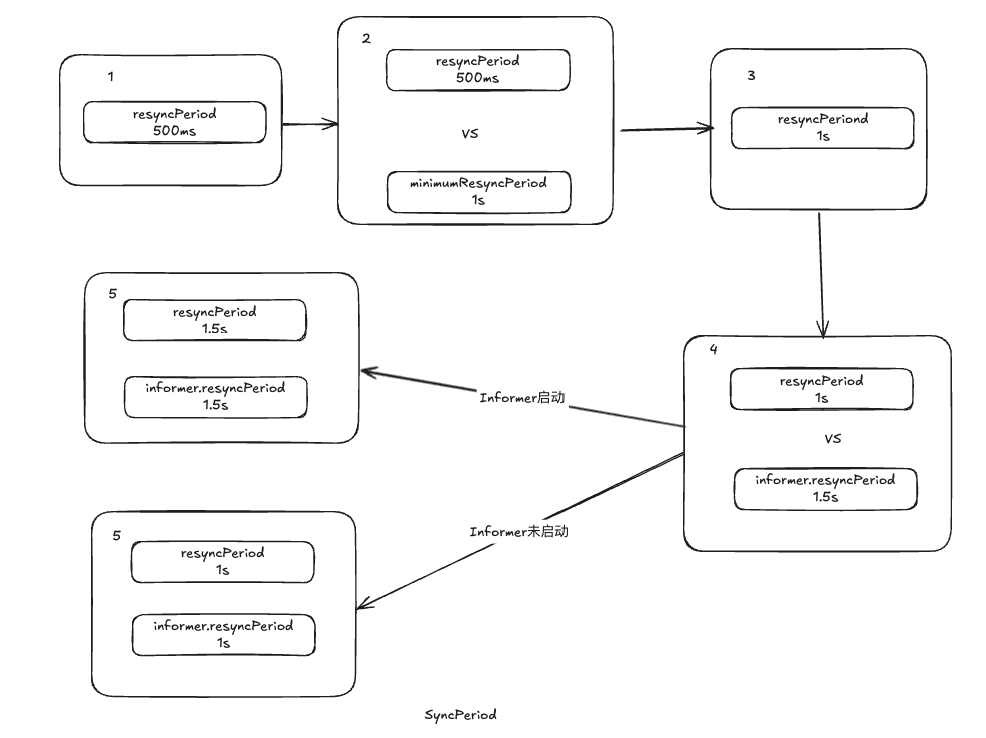
if resyncPeriod > 0 {
if resyncPeriod < minimumResyncPeriod {
klog.Warningf("resyncPeriod %v is too small. Changing it to the minimum allowed value of %v", resyncPeriod, minimumResyncPeriod)
resyncPeriod = minimumResyncPeriod
}
if resyncPeriod < s.resyncCheckPeriod {
if s.started {
klog.Warningf("resyncPeriod %v is smaller than resyncCheckPeriod %v and the informer has already started. Changing it to %v", resyncPeriod, s.resyncCheckPeriod, s.resyncCheckPeriod)
resyncPeriod = s.resyncCheckPeriod
} else {
// if the event handler's resyncPeriod is smaller than the current resyncCheckPeriod, update
// resyncCheckPeriod to match resyncPeriod and adjust the resync periods of all the listeners
// accordingly
s.resyncCheckPeriod = resyncPeriod
s.processor.resyncCheckPeriodChanged(resyncPeriod)
}
}
}
listener := newProcessListener(handler, resyncPeriod, determineResyncPeriod(resyncPeriod, s.resyncCheckPeriod), s.clock.Now(), initialBufferSize)
if !s.started {
s.processor.addListener(listener)
return
}
// in order to safely join, we have to
// 1. stop sending add/update/delete notifications
// 2. do a list against the store
// 3. send synthetic "Add" events to the new handler
// 4. unblock
s.blockDeltas.Lock()
defer s.blockDeltas.Unlock()
s.processor.addListener(listener)
for _, item := range s.indexer.List() {
listener.add(addNotification{newObj: item})
}
}
监听器缓冲机制
processorListener用于处理资源对象变更数据的监听器,接收匆匆HandleDeltas func从DeltaFIFO中获取的资源对象操作记录,交给ResourceHandler进行处理,可以处理以下的事件:
- addNotification:新增资源对象通知消息,其中包含完整的新添加的资源对象newObj
- updateNotification:更新资源对象通知消息,其中包含完整的添加的资源对象newObj和旧资源对象oldObj
- deleteNotification:删除资源对象通知消息,其中包含完整的旧资源对象oldObj
为了实现资源对象操作事件的高效无阻塞处理,引入了俩个无缓冲输入通道配合环形缓存队列
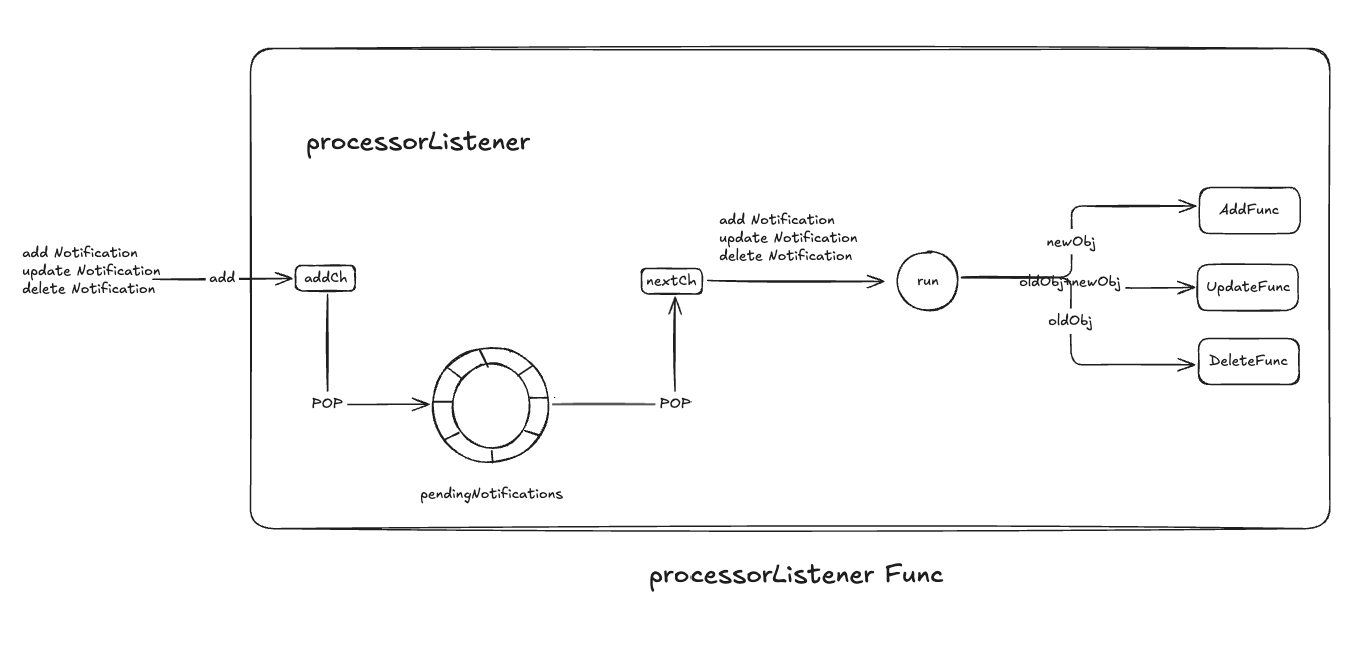
- processorListener会在一个独立的gouroutine执行pop,同时监听输入addCh和输出nextCh
- 把输入写到环形缓存队列中,pendingNotifications
- 读取环形缓存对象,写入输出nextCh
- processListener在另外一个gouroutine执行tun,不断轮训nextCh中的事件,根据时间调用ResourceEventHandler对应的事件
workqueue工作队列
workqueue主要用于标记和去重复
- 有序:按照添加顺序处理元素
- 去重:相同元素在同一时间不会被重复处理
- 并发:支持多个生产者和消费者
- 标记机制:支持标记功能,标记一个元素是否被处理,也允许元素在处理时重新排队
- 通知策略:ShutDown 方法通过信号量通知队列不再接收新元素,并且通知metric goroutine退出
- 限速:支持限速策略,在元素存入队列的时进行速率限制。限制一个元素重新排队的次数
- Metric:支持metric指标,可用于Prometheus健康
- 支持三种队列
- Interface:FIFO通用用队列列接口,先进先出,并且支持去重机制
- DelayingInterface:延迟队列接口,基于Interface,延迟一段时间插入队列
- RaceLimiting Interface:限速队列接口,基于Delaying Interface,支持插入队列的时候限速
FIFO通用队列
FIFO通用队列实现队列的基本操作
-
type Interface interface {
// 添加元素
Add(item interface{})
// 获取队列长度
Len() int
// 获取队列头部元素
Get() (item interface{}, shutdown bool)
// 把队列元素标记为已经处理
Done(item interface{})
// 关闭队列。停止添加元素,马上结束队列中所有的goroutine
ShutDown()
// 排空队列,再退出
ShutDownWithDrain()
// 查询队列是否正在关闭
ShuttingDown() bool
}
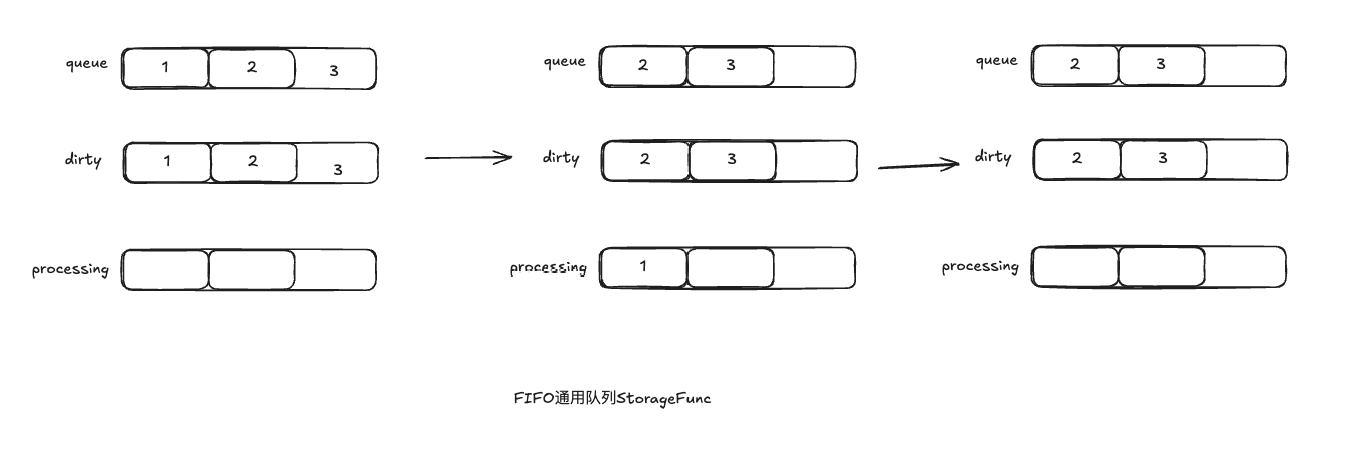
通用队列数据结构:
-
// Type is a work queue (see the package comment).
type Type struct {
// queue defines the order in which we will work on items. Every
// element of queue should be in the dirty set and not in the
// processing set.
// 实际存储队列元素
queue []t
// dirty defines all of the items that need to be processed.
// 保证去重
dirty set
// Things that are currently being processed are in the processing set.
// These things may be simultaneously in the dirty set. When we finish
// processing something and remove it from this set, we'll check if
// it's in the dirty set, and if so, add it to the queue.
// 标记是否正在处理
processing set
cond *sync.Cond
shuttingDown bool
drain bool
metrics queueMetrics
unfinishedWorkUpdatePeriod time.Duration
clock clock.WithTicker
}
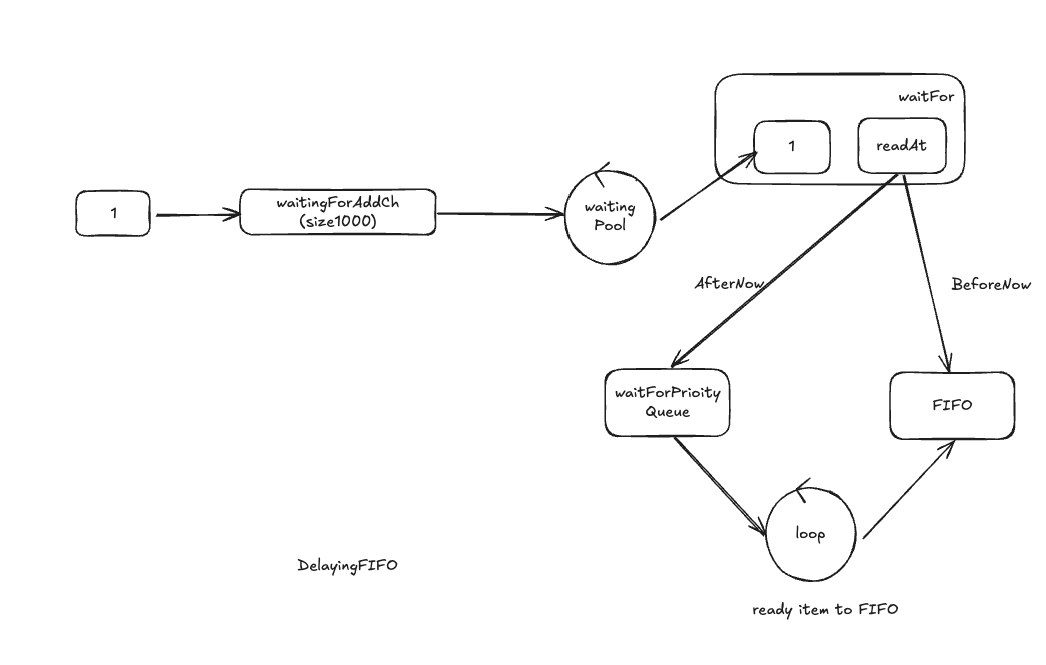
延迟队列
在通用队列上添加了AddAfter func
-
// DelayingInterface is an Interface that can Add an item at a later time. This makes it easier to
// requeue items after failures without ending up in a hot-loop.
type DelayingInterface interface {
Interface
// AddAfter adds an item to the workqueue after the indicated duration has passed
// 插入一个item元素,并且附加一个duration延迟时间,如果duration小于等于0 直接插入
AddAfter(item interface{}, duration time.Duration)
}
延迟队列数据结构:
-
// delayingType wraps an Interface and provides delayed re-enquing
type delayingType struct {
Interface
// clock tracks time for delayed firing
clock clock.Clock
// stopCh lets us signal a shutdown to the waiting loop
stopCh chan struct{}
// stopOnce guarantees we only signal shutdown a single time
stopOnce sync.Once
// heartbeat ensures we wait no more than maxWait before firing
heartbeat clock.Ticker
// waitingForAddCh is a buffered channel that feeds waitingForAdd
waitingForAddCh chan *waitFor
// metrics counts the number of retries
metrics retryMetrics
}
限速队列(ReteLimitInterface)
在延迟队列基础上,添加了AddRateLimit、Forget、NumRequeues func,提供了四种限速策略
-
// RateLimitingInterface is an interface that rate limits items being added to the queue.
type RateLimitingInterface interface {
DelayingInterface
// AddRateLimited adds an item to the workqueue after the rate limiter says it's ok
AddRateLimited(item interface{})
// Forget indicates that an item is finished being retried. Doesn't matter whether it's for perm failing
// or for success, we'll stop the rate limiter from tracking it. This only clears the `rateLimiter`, you
// still have to call `Done` on the queue.
Forget(item interface{})
// NumRequeues returns back how many times the item was requeued
NumRequeues(item interface{}) int
}
限速算法概述
限速接口
-
type RateLimiter interface {
// When gets an item and gets to decide how long that item should wait
// 获取指定元素应该等待的时间
When(item interface{}) time.Duration
// Forget indicates that an item is finished being retried. Doesn't matter whether it's for failing
// or for success, we'll stop tracking it
// 释放指定元素,清空该元素的排队数
Forget(item interface{})
// NumRequeues returns back how many failures the item has had
// 获取指定元素的排队数
NumRequeues(item interface{}) int
}
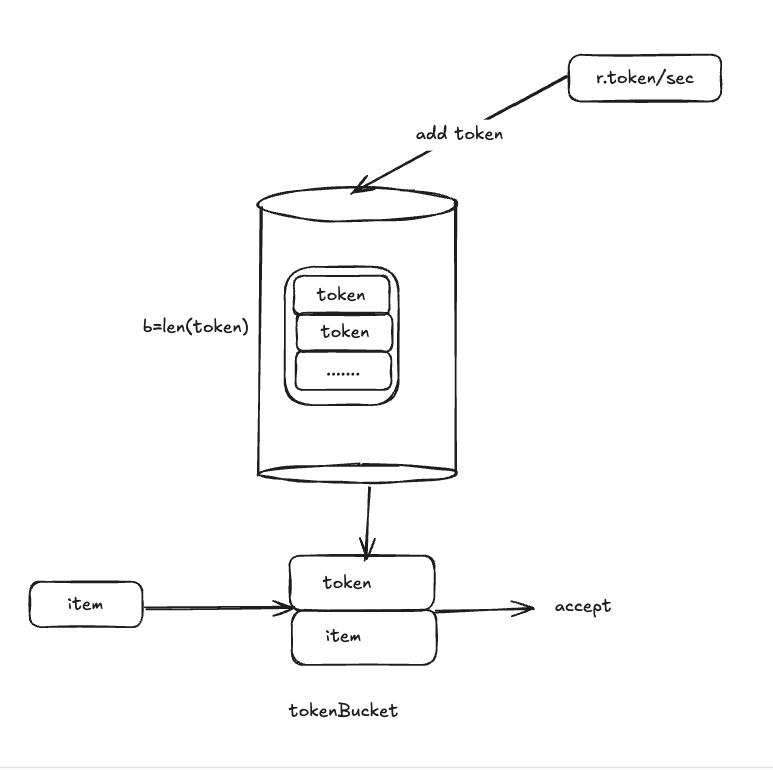
令牌桶算法
令牌桶算法基于了golang.org/x/rate实现
令牌桶算法内部实现了一个存放token 的桶
初始化,桶中有一定数量的token,此后固定速率添加token到桶中,直至桶满,多余token被丢弃
每个元素都会从令牌桶中获取token,只有有token的时元素才能被通过
-
// DefaultControllerRateLimiter is a no-arg constructor for a default rate limiter for a workqueue. It has
// both overall and per-item rate limiting. The overall is a token bucket and the per-item is exponential
func DefaultControllerRateLimiter() RateLimiter {
return NewMaxOfRateLimiter(
NewItemExponentialFailureRateLimiter(5*time.Millisecond, 1000*time.Second),
// 10 qps, 100 bucket size. This is only for retry speed and its only the overall factor (not per item)
// 获取令牌桶
&BucketRateLimiter{Limiter: rate.NewLimiter(rate.Limit(10), 100)},
)
}
排队指数算法
排队指数算法把相同元素的排队数作为指数,排队数增大,速度限制指数级增长,但是最大值不会超过maxDelay
在同一个限速周期内,不存在相同元素,所有延迟时间为baseDelay,如果有存在,相同元素延迟时间延迟指数级别增大
-
func (r *ItemExponentialFailureRateLimiter) When(item interface{}) time.Duration {
r.failuresLock.Lock()
defer r.failuresLock.Unlock()
exp := r.failures[item]
r.failures[item] = r.failures[item] + 1
// The backoff is capped such that 'calculated' value never overflows.
backoff := float64(r.baseDelay.Nanoseconds()) * math.Pow(2, float64(exp))
if backoff > math.MaxInt64 {
return r.maxDelay
}
calculated := time.Duration(backoff)
if calculated > r.maxDelay {
return r.maxDelay
}
return calculated
}
计数器算法
限制一段时间内允许通过的元素量,同时拓展了fast和slow速率
没有达到限速数量,使用fast速率,达到数量,使用slow速率
混合算法
混合使用以上多种限速速率
// DefaultControllerRateLimiter is a no-arg constructor for a default rate limiter for a workqueue. It has |


