K8s-etcd核心存储实现
K8s-etcd核心存储实现
基于1.25
什么是Etcd
etcd是K8s默认的数据持久化端存储,主要用于保存集群配置和状态
- etcd是分布式键值存储集群
- 基于Raft协议提供可靠强一致性数据存取服务
架构设计
REST Storage
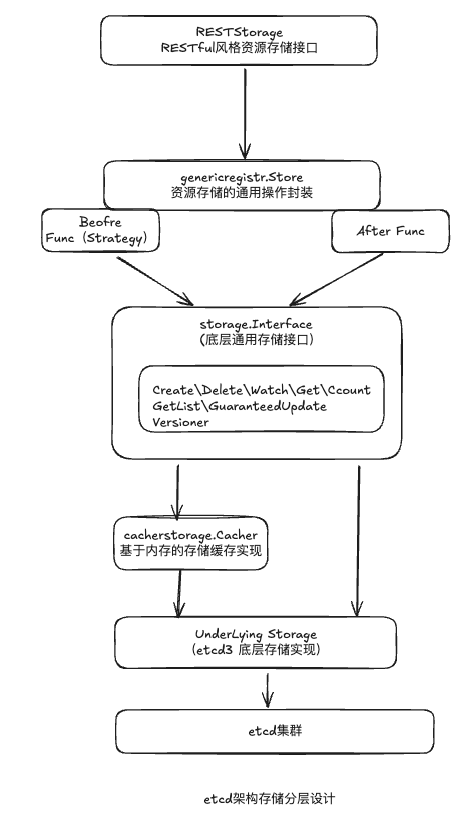
genericregistory.Store
genericregistory.Store封装了资源对象的CRUD操作,并且支持资源版本ResourceVersion的冲突检查
- 在存储资源对象前执行Beofre Func,存储资源对象后执行(After Func),以及处理DryRun
storage.Interface
底层通用存储接口,定义了资源的操作方法,Create|Delete|Watch|Get|Count|GETList|GuranteedUpdate|Versioner
cachestorage.Cacher
为了减轻etcd读取压力和提供了Cache,可以通过设置kube-apiserver的–watch-cache启动或者关闭Cacher,默认开启
Underlying Storage
后端存储,默认K8s使用etcd3,使用etcd client库实现storage.Interface
RESTStorage资源存储接口
K8s中,所有都通过Kube-apiserver RESTful API对外暴露资源,必须实现RESTSTorage才能对外注册到APIGroup
-
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13// Storage is a generic interface for RESTful storage services.
// Resources which are exported to the RESTful API of apiserver need to implement this interface. It is expected
// that objects may implement any of the below interfaces.
type Storage interface {
// New returns an empty object that can be used with Create and Update after request data has been put into it.
// This object must be a pointer type for use with Codec.DecodeInto([]byte, runtime.Object)
New() runtime.Object
// Destroy cleans up its resources on shutdown.
// Destroy has to be implemented in thread-safe way and be prepared
// for being called more than once.
Destroy()
}
可能还有获取到实时资源对象变化的能力:
-
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9// Watcher should be implemented by all Storage objects that
// want to offer the ability to watch for changes through the watch api.
type Watcher interface {
// 'label' selects on labels; 'field' selects on the object's fields. Not all fields
// are supported; an error should be returned if 'field' tries to select on a field that
// isn't supported. 'resourceVersion' allows for continuing/starting a watch at a
// particular version.
Watch(ctx context.Context, options *metainternalversion.ListOptions) (watch.Interface, error)
}
在K8s中,每种资源实现的RESTStorage,一般定义在pkg/registry/<资源组>/<资源>/storage/storage.go,通过NewREST或NewStorage实例化函数RESTStorage接口
-
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27// DeploymentStorage includes dummy storage for Deployments and for Scale subresource.
type DeploymentStorage struct {
Deployment *REST
Status *StatusREST
Scale *ScaleREST
Rollback *RollbackREST
}
// NewStorage returns new instance of DeploymentStorage.
func NewStorage(optsGetter generic.RESTOptionsGetter) (DeploymentStorage, error) {
deploymentRest, deploymentStatusRest, deploymentRollbackRest, err := NewREST(optsGetter)
if err != nil {
return DeploymentStorage{}, err
}
return DeploymentStorage{
Deployment: deploymentRest,
Status: deploymentStatusRest,
Scale: &ScaleREST{store: deploymentRest.Store},
Rollback: deploymentRollbackRest,
}, nil
}
// REST implements a RESTStorage for Deployments.
type REST struct {
*genericregistry.Store
}
genericregistry.Store通用操作封装
对一般的资源对象的通用操作进行了抽象和封装。形成了genericregistery.Store
- 有常规的资源存储需要
- 自动处理资源更新时的版本冲突检查
- 存储前后的钩子函数
- 支持服务端DryRun模式
标准存储实现
genericregistry.Store同时实现了StandardStorage和TableConvertor接口
StandardStorage:对基本的RESTStorage的拓展
TableConvertor:主要用于将资源对象列表转换为用户更好的表格形式
-
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15// StandardStorage is an interface covering the common verbs. Provided for testing whether a
// resource satisfies the normal storage methods. Use Storage when passing opaque storage objects.
type StandardStorage interface {
Getter
Lister
CreaterUpdater
GracefulDeleter
CollectionDeleter
Watcher
// Destroy cleans up its resources on shutdown.
// Destroy has to be implemented in thread-safe way and be prepared
// for being called more than once.
Destroy()
} -
1
2
3type TableConvertor interface {
ConvertToTable(ctx context.Context, object runtime.Object, tableOptions runtime.Object) (*metav1.Table, error)
}
版本冲突检测
genericregistry.Store在执行资源更新的时候采用了乐观锁,通过对比更新前后资源的版本对象的Resource.Version是否变换判断本次更新是否冲突
多并发场景下,乐观锁能有效避免脏数据,K8s资源对象更新都会增大ResourceVersion
-
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9// Update performs an atomic update and set of the object. Returns the result of the update
// or an error. If the registry allows create-on-update, the create flow will be executed.
// A bool is returned along with the object and any errors, to indicate object creation.
func (e *Store) Update(ctx context.Context, name string, objInfo rest.UpdatedObjectInfo, createValidation rest.ValidateObjectFunc, updateValidation rest.ValidateObjectUpdateFunc, forceAllowCreate bool, options *metav1.UpdateOptions) (runtime.Object, bool, error) {
key, err := e.KeyFunc(ctx, name)
if err != nil {
return nil, false, err
}
...
通用钩子函数
-
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135type Store struct {
// NewFunc returns a new instance of the type this registry returns for a
// GET of a single object, e.g.:
//
// curl GET /apis/group/version/namespaces/my-ns/myresource/name-of-object
NewFunc func() runtime.Object
// NewListFunc returns a new list of the type this registry; it is the
// type returned when the resource is listed, e.g.:
//
// curl GET /apis/group/version/namespaces/my-ns/myresource
NewListFunc func() runtime.Object
// DefaultQualifiedResource is the pluralized name of the resource.
// This field is used if there is no request info present in the context.
// See qualifiedResourceFromContext for details.
DefaultQualifiedResource schema.GroupResource
// KeyRootFunc returns the root etcd key for this resource; should not
// include trailing "/". This is used for operations that work on the
// entire collection (listing and watching).
//
// KeyRootFunc and KeyFunc must be supplied together or not at all.
KeyRootFunc func(ctx context.Context) string
// KeyFunc returns the key for a specific object in the collection.
// KeyFunc is called for Create/Update/Get/Delete. Note that 'namespace'
// can be gotten from ctx.
//
// KeyFunc and KeyRootFunc must be supplied together or not at all.
KeyFunc func(ctx context.Context, name string) (string, error)
// ObjectNameFunc returns the name of an object or an error.
ObjectNameFunc func(obj runtime.Object) (string, error)
// TTLFunc returns the TTL (time to live) that objects should be persisted
// with. The existing parameter is the current TTL or the default for this
// operation. The update parameter indicates whether this is an operation
// against an existing object.
//
// Objects that are persisted with a TTL are evicted once the TTL expires.
TTLFunc func(obj runtime.Object, existing uint64, update bool) (uint64, error)
// PredicateFunc returns a matcher corresponding to the provided labels
// and fields. The SelectionPredicate returned should return true if the
// object matches the given field and label selectors.
PredicateFunc func(label labels.Selector, field fields.Selector) storage.SelectionPredicate
// EnableGarbageCollection affects the handling of Update and Delete
// requests. Enabling garbage collection allows finalizers to do work to
// finalize this object before the store deletes it.
//
// If any store has garbage collection enabled, it must also be enabled in
// the kube-controller-manager.
EnableGarbageCollection bool
// DeleteCollectionWorkers is the maximum number of workers in a single
// DeleteCollection call. Delete requests for the items in a collection
// are issued in parallel.
DeleteCollectionWorkers int
// Decorator is an optional exit hook on an object returned from the
// underlying storage. The returned object could be an individual object
// (e.g. Pod) or a list type (e.g. PodList). Decorator is intended for
// integrations that are above storage and should only be used for
// specific cases where storage of the value is not appropriate, since
// they cannot be watched.
// 退出钩子,从底层存储获取到资源对象后,返回给调用者进行最后的修正
// 只适合一些特殊的场景,如底层存储的资源对象不能直接满足调用者要求(如不支持watch)
Decorator func(runtime.Object)
// CreateStrategy implements resource-specific behavior during creation.
CreateStrategy rest.RESTCreateStrategy
// BeginCreate is an optional hook that returns a "transaction-like"
// commit/revert function which will be called at the end of the operation,
// but before AfterCreate and Decorator, indicating via the argument
// whether the operation succeeded. If this returns an error, the function
// is not called. Almost nobody should use this hook.
// 存储之前的func
BeginCreate BeginCreateFunc
// AfterCreate implements a further operation to run after a resource is
// created and before it is decorated, optional.
// 存储之后的func
AfterCreate AfterCreateFunc
// UpdateStrategy implements resource-specific behavior during updates.
UpdateStrategy rest.RESTUpdateStrategy
// BeginUpdate is an optional hook that returns a "transaction-like"
// commit/revert function which will be called at the end of the operation,
// but before AfterUpdate and Decorator, indicating via the argument
// whether the operation succeeded. If this returns an error, the function
// is not called. Almost nobody should use this hook.
BeginUpdate BeginUpdateFunc
// AfterUpdate implements a further operation to run after a resource is
// updated and before it is decorated, optional.
AfterUpdate AfterUpdateFunc
// DeleteStrategy implements resource-specific behavior during deletion.
DeleteStrategy rest.RESTDeleteStrategy
// AfterDelete implements a further operation to run after a resource is
// deleted and before it is decorated, optional.
AfterDelete AfterDeleteFunc
// ReturnDeletedObject determines whether the Store returns the object
// that was deleted. Otherwise, return a generic success status response.
ReturnDeletedObject bool
// ShouldDeleteDuringUpdate is an optional function to determine whether
// an update from existing to obj should result in a delete.
// If specified, this is checked in addition to standard finalizer,
// deletionTimestamp, and deletionGracePeriodSeconds checks.
ShouldDeleteDuringUpdate func(ctx context.Context, key string, obj, existing runtime.Object) bool
// TableConvertor is an optional interface for transforming items or lists
// of items into tabular output. If unset, the default will be used.
TableConvertor rest.TableConvertor
// ResetFieldsStrategy provides the fields reset by the strategy that
// should not be modified by the user.
ResetFieldsStrategy rest.ResetFieldsStrategy
// Storage is the interface for the underlying storage for the
// resource. It is wrapped into a "DryRunnableStorage" that will
// either pass-through or simply dry-run.
Storage DryRunnableStorage
// StorageVersioner outputs the <group/version/kind> an object will be
// converted to before persisted in etcd, given a list of possible
// kinds of the object.
// If the StorageVersioner is nil, apiserver will leave the
// storageVersionHash as empty in the discovery document.
StorageVersioner runtime.GroupVersioner
// DestroyFunc cleans up clients used by the underlying Storage; optional.
// If set, DestroyFunc has to be implemented in thread-safe way and
// be prepared for being called more than once.
DestroyFunc func()
}
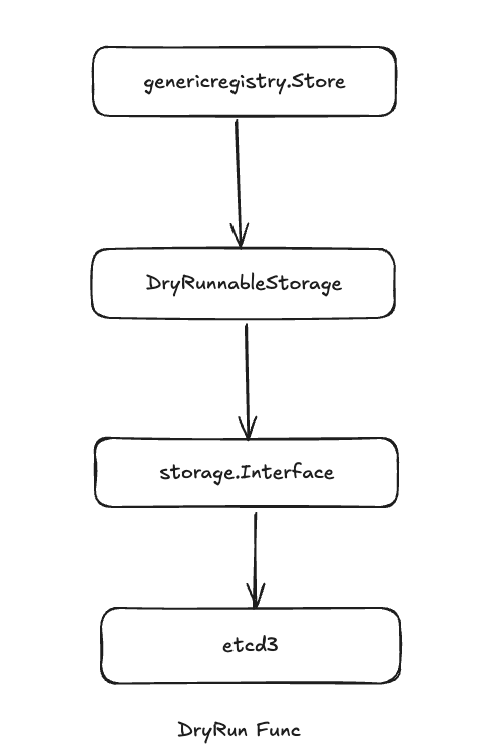
DryRun实现原理
kubectl中的--dry-run可以帮我们真正执行操作前检查应用配置是否存在错误或者冲突
-
1
2
3
4type DryRunnableStorage struct {
Storage storage.Interface
Codec runtime.Codec
} -
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9func (s *DryRunnableStorage) Create(ctx context.Context, key string, obj, out runtime.Object, ttl uint64, dryRun bool) error {
if dryRun {
if err := s.Storage.Get(ctx, key, storage.GetOptions{}, out); err == nil {
return storage.NewKeyExistsError(key, 0)
}
return s.copyInto(obj, out)
}
return s.Storage.Create(ctx, key, obj, out, ttl)
}
storage.Interface通用存储接口
-
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
// Interface offers a common interface for object marshaling/unmarshaling operations and
// hides all the storage-related operations behind it.
type Interface interface {
// Returns Versioner associated with this interface.
// 资源版本管理器,包含从底层存储读取资源对象的版本信息以及写入资源对象的ResourceVersion
Versioner() Versioner
// Create adds a new object at a key unless it already exists. 'ttl' is time-to-live
// in seconds (0 means forever). If no error is returned and out is not nil, out will be
// set to the read value from database.
// 创建资源对象,支持传入TTL,传入0代表永远不过期,Event资源对象默认保留1h(设置了1h的ttl)
Create(ctx context.Context, key string, obj, out runtime.Object, ttl uint64) error
// Delete removes the specified key and returns the value that existed at that spot.
// If key didn't exist, it will return NotFound storage error.
// If 'cachedExistingObject' is non-nil, it can be used as a suggestion about the
// current version of the object to avoid read operation from storage to get it.
// However, the implementations have to retry in case suggestion is stale.
// 删除资源对象的函数
Delete(
ctx context.Context, key string, out runtime.Object, preconditions *Preconditions,
validateDeletion ValidateObjectFunc, cachedExistingObject runtime.Object) error
// Watch begins watching the specified key. Events are decoded into API objects,
// and any items selected by 'p' are sent down to returned watch.Interface.
// resourceVersion may be used to specify what version to begin watching,
// which should be the current resourceVersion, and no longer rv+1
// (e.g. reconnecting without missing any updates).
// If resource version is "0", this interface will get current object at given key
// and send it in an "ADDED" event, before watch starts.
// 通过Watch机制监听资源对象的函数,只应用于单个key
Watch(ctx context.Context, key string, opts ListOptions) (watch.Interface, error)
// Get unmarshals object found at key into objPtr. On a not found error, will either
// return a zero object of the requested type, or an error, depending on 'opts.ignoreNotFound'.
// Treats empty responses and nil response nodes exactly like a not found error.
// The returned contents may be delayed, but it is guaranteed that they will
// match 'opts.ResourceVersion' according 'opts.ResourceVersionMatch'.
// 获取资源对象的函数
Get(ctx context.Context, key string, opts GetOptions, objPtr runtime.Object) error
// GetList unmarshalls objects found at key into a *List api object (an object
// that satisfies runtime.IsList definition).
// If 'opts.Recursive' is false, 'key' is used as an exact match. If `opts.Recursive'
// is true, 'key' is used as a prefix.
// The returned contents may be delayed, but it is guaranteed that they will
// match 'opts.ResourceVersion' according 'opts.ResourceVersionMatch'.
// 获取资源对象列表
GetList(ctx context.Context, key string, opts ListOptions, listObj runtime.Object) error
// GuaranteedUpdate keeps calling 'tryUpdate()' to update key 'key' (of type 'destination')
// retrying the update until success if there is index conflict.
// Note that object passed to tryUpdate may change across invocations of tryUpdate() if
// other writers are simultaneously updating it, so tryUpdate() needs to take into account
// the current contents of the object when deciding how the update object should look.
// If the key doesn't exist, it will return NotFound storage error if ignoreNotFound=false
// else `destination` will be set to the zero value of it's type.
// If the eventual successful invocation of `tryUpdate` returns an output with the same serialized
// contents as the input, it won't perform any update, but instead set `destination` to an object with those
// contents.
// If 'cachedExistingObject' is non-nil, it can be used as a suggestion about the
// current version of the object to avoid read operation from storage to get it.
// However, the implementations have to retry in case suggestion is stale.
//
// Example:
//
// s := /* implementation of Interface */
// err := s.GuaranteedUpdate(
// "myKey", &MyType{}, true, preconditions,
// func(input runtime.Object, res ResponseMeta) (runtime.Object, *uint64, error) {
// // Before each invocation of the user defined function, "input" is reset to
// // current contents for "myKey" in database.
// curr := input.(*MyType) // Guaranteed to succeed.
//
// // Make the modification
// curr.Counter++
//
// // Return the modified object - return an error to stop iterating. Return
// // a uint64 to alter the TTL on the object, or nil to keep it the same value.
// return cur, nil, nil
// }, cachedExistingObject
// )
// 更新资源对象,会通过重试调用传入的tryUpdate func
GuaranteedUpdate(
ctx context.Context, key string, destination runtime.Object, ignoreNotFound bool,
preconditions *Preconditions, tryUpdate UpdateFunc, cachedExistingObject runtime.Object) error
// Count returns number of different entries under the key (generally being path prefix).
// 获取指定key下的条目数量
Count(key string) (int64, error)
}
Cacher Storage缓存层
Cacher Storage可以减少数据库服务负载,减少连接数等
Cacher Storage缓存架构
Cacher Storage缓存层通过对底层数据进行缓存,提高etcd集群的响应速度,同时减少底层etcd集群连接数,确保缓存数据与etcd集群中数据保持一致
Cacher Storage缓存层缓存范围:
- Get、Get List、Watch、GuaranteedUpdate、Delete等操作
- 不包含:Create、Count、Versioner等操作
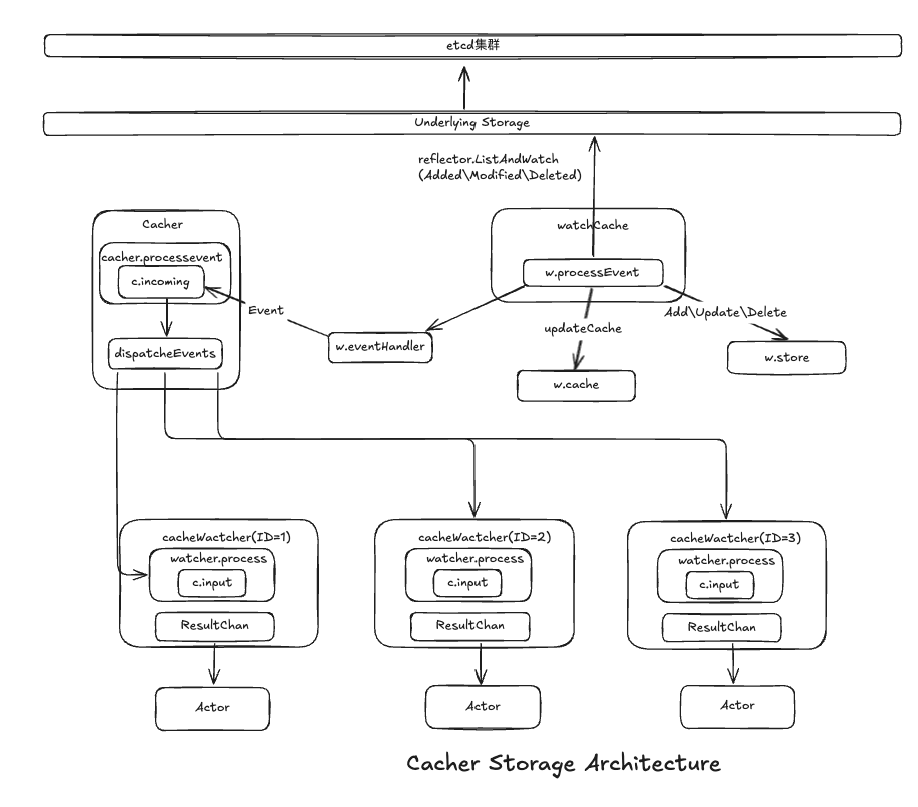
watchCache
watchCache是缓存架构基于Reflector框架的ListAndWatch func通过Underlying Storage 监听etcd集群的事件
-
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29func (c *Cacher) startCaching(stopChannel <-chan struct{}) {
// The 'usable' lock is always 'RLock'able when it is safe to use the cache.
// It is safe to use the cache after a successful list until a disconnection.
// We start with usable (write) locked. The below OnReplace function will
// unlock it after a successful list. The below defer will then re-lock
// it when this function exits (always due to disconnection), only if
// we actually got a successful list. This cycle will repeat as needed.
successfulList := false
c.watchCache.SetOnReplace(func() {
successfulList = true
c.ready.set(true)
klog.V(1).Infof("cacher (%v): initialized", c.objectType.String())
metrics.WatchCacheInitializations.WithLabelValues(c.objectType.String()).Inc()
})
defer func() {
if successfulList {
c.ready.set(false)
}
}()
c.terminateAllWatchers()
// Note that since onReplace may be not called due to errors, we explicitly
// need to retry it on errors under lock.
// Also note that startCaching is called in a loop, so there's no need
// to have another loop here.
if err := c.reflector.ListAndWatch(stopChannel); err != nil {
klog.Errorf("cacher (%v): unexpected ListAndWatch error: %v; reinitializing...", c.objectType.String(), err)
}
}
reflector框架提供了接收事件回调:实现了Add、Update、Delete函数
w.store:接收到事件存储到本地缓存,数据结构为cache.Indexer,功能与client-go到Indexer相同
w.cache:是一个环形缓存队列,将事件存储至缓存滑动窗口,提供对Watch 操作的缓存数据,防止因为网络或其他原因Watch连接中断,导致事件丢失
w.eventHandler:把事件分发给Cacher,Cacher进一步将事件二级分发给目前所有已建立连接Watcher,分发过程使用非阻塞式
-
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60// processEvent is safe as long as there is at most one call to it in flight
// at any point in time.
func (w *watchCache) processEvent(event watch.Event, resourceVersion uint64, updateFunc func(*storeElement) error) error {
key, err := w.keyFunc(event.Object)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("couldn't compute key: %v", err)
}
elem := &storeElement{Key: key, Object: event.Object}
elem.Labels, elem.Fields, err = w.getAttrsFunc(event.Object)
if err != nil {
return err
}
wcEvent := &watchCacheEvent{
Type: event.Type,
Object: elem.Object,
ObjLabels: elem.Labels,
ObjFields: elem.Fields,
Key: key,
ResourceVersion: resourceVersion,
RecordTime: w.clock.Now(),
}
if err := func() error {
// TODO: We should consider moving this lock below after the watchCacheEvent
// is created. In such situation, the only problematic scenario is Replace(
// happening after getting object from store and before acquiring a lock.
// Maybe introduce another lock for this purpose.
w.Lock()
defer w.Unlock()
previous, exists, err := w.store.Get(elem)
if err != nil {
return err
}
if exists {
previousElem := previous.(*storeElement)
wcEvent.PrevObject = previousElem.Object
wcEvent.PrevObjLabels = previousElem.Labels
wcEvent.PrevObjFields = previousElem.Fields
}
w.updateCache(wcEvent)
w.resourceVersion = resourceVersion
defer w.cond.Broadcast()
return updateFunc(elem)
}(); err != nil {
return err
}
// Avoid calling event handler under lock.
// This is safe as long as there is at most one call to Add/Update/Delete and
// UpdateResourceVersion in flight at any point in time, which is true now,
// because reflector calls them synchronously from its main thread.
if w.eventHandler != nil {
w.eventHandler(wcEvent)
}
return nil
}
Cacher
Cacher把接收到的watchCache回调发送过来的事件后,遍历目前所有已经连接的Watcher,并且把事件逐个分发给每个Watcher,分发过程使用非阻塞
-
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8func (c *cacheWatcher) nonblockingAdd(event *watchCacheEvent) bool {
select {
case c.input <- event:
return true
default:
return false
}
}
这里的非阻塞式是相对的,优先采用非阻塞
为了容忍短暂的连接异常,当非阻塞失败事件转发,K8s首先尝试设置一个定时器,延迟发送时间,当定时器延迟发送超时还是没有事件发送,才会关闭对应的Broker Watch连接
cacheWatcher
kube-apiserver会为每个watch请求的客户端发起一个独立的cacheWatcher实例,用于接收Watch事件
-
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39// Watch implements storage.Interface.
func (c *Cacher) Watch(ctx context.Context, key string, opts storage.ListOptions) (watch.Interface, error) {
...
// Create a watcher here to reduce memory allocations under lock,
// given that memory allocation may trigger GC and block the thread.
// Also note that emptyFunc is a placeholder, until we will be able
// to compute watcher.forget function (which has to happen under lock).
watcher := newCacheWatcher(chanSize, filterWithAttrsFunction(key, pred), emptyFunc, c.versioner, deadline, pred.AllowWatchBookmarks, c.objectType, identifier)
// We explicitly use thread unsafe version and do locking ourself to ensure that
// no new events will be processed in the meantime. The watchCache will be unlocked
// on return from this function.
// Note that we cannot do it under Cacher lock, to avoid a deadlock, since the
// underlying watchCache is calling processEvent under its lock.
c.watchCache.RLock()
defer c.watchCache.RUnlock()
cacheInterval, err := c.watchCache.getAllEventsSinceLocked(watchRV)
if err != nil {
// To match the uncached watch implementation, once we have passed authn/authz/admission,
// and successfully parsed a resource version, other errors must fail with a watch event of type ERROR,
// rather than a directly returned error.
return newErrWatcher(err), nil
}
func() {
c.Lock()
defer c.Unlock()
// Update watcher.forget function once we can compute it.
watcher.forget = forgetWatcher(c, watcher, c.watcherIdx, triggerValue, triggerSupported)
c.watchers.addWatcher(watcher, c.watcherIdx, triggerValue, triggerSupported)
// Add it to the queue only when the client support watch bookmarks.
if watcher.allowWatchBookmarks {
c.bookmarkWatchers.addWatcher(watcher)
}
c.watcherIdx++
}()
...
}
当客户端发起Watch请求,通过newCacheWatcher func 实例化cacheWatcher对象,并分配一个ID。这个ID全局唯一,从0开始计数,当有新的客户端发送Watch请求,ID自增1.kube-apiserver重启重置。
Cacher通过map维护cacherWatcher实例,key为ID,value为cacheWatcher
-
1
type watchersMap map[int]*cacheWatcher
在cacherWatcher初始化,会同时启动一个goroutine协程,最终调用watcher.process func,监听c.input.channel中的数据,当其中没有数据,会进入阻塞;其他有数据,通过ResultChan对外暴露,只发送大于ResourceVersion
-
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24func (c *cacheWatcher) process(ctx context.Context, resourceVersion uint64) {
// At this point we already start processing incoming watch events.
// However, the init event can still be processed because their serialization
// and sending to the client happens asynchrnously.
// TODO: As describe in the KEP, we would like to estimate that by delaying
// the initialization signal proportionally to the number of events to
// process, but we're leaving this to the tuning phase.
utilflowcontrol.WatchInitialized(ctx)
for {
select {
case event, ok := <-c.input:
if !ok {
return
}
// only send events newer than resourceVersion
if event.ResourceVersion > resourceVersion {
c.sendWatchCacheEvent(event)
}
case <-ctx.Done():
return
}
}
}
ReourceVersion资源版本号
ReourceVersion是K8s资源对象中非常重要的元素
- 用于资源更新的冲突检测
- 在List和Watch阶段防止事件丢失
- 每次对etcd中资源对象修改的时候,都会更新ResourceVersion
- Client-go根据ResourceVersion就可以标志资源对象是否变化
- 如果Watch意外端开,从上次的ResourceVersion开始重新监听,确保Watch连贯
K8s没有对ResourceVersion有额外的实现,依赖etcd的全局Indexer实例,有俩个核心的Indexer,分为createdIndex和modifiedIndex
- createdIndex:全局唯一且递增的正整数,每次在etcd集群中创建key时就会递增
- modifiedIndex:与createdIndex相视,但是每次对etcd集群中的key进行修改的时候递增
- createdIndex和modifiedIndex都通过原子操作更新
以storage.Interface Get为例:
-
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31// Get implements storage.Interface.Get.
func (s *store) Get(ctx context.Context, key string, opts storage.GetOptions, out runtime.Object) error {
preparedKey, err := s.prepareKey(key)
if err != nil {
return err
}
startTime := time.Now()
getResp, err := s.client.KV.Get(ctx, preparedKey)
metrics.RecordEtcdRequestLatency("get", getTypeName(out), startTime)
if err != nil {
return err
}
if err = s.validateMinimumResourceVersion(opts.ResourceVersion, uint64(getResp.Header.Revision)); err != nil {
return err
}
if len(getResp.Kvs) == 0 {
if opts.IgnoreNotFound {
return runtime.SetZeroValue(out)
}
return storage.NewKeyNotFoundError(preparedKey, 0)
}
kv := getResp.Kvs[0]
data, _, err := s.transformer.TransformFromStorage(ctx, kv.Value, authenticatedDataString(preparedKey))
if err != nil {
return storage.NewInternalError(err.Error())
}
return decode(s.codec, s.versioner, data, out, kv.ModRevision)
}
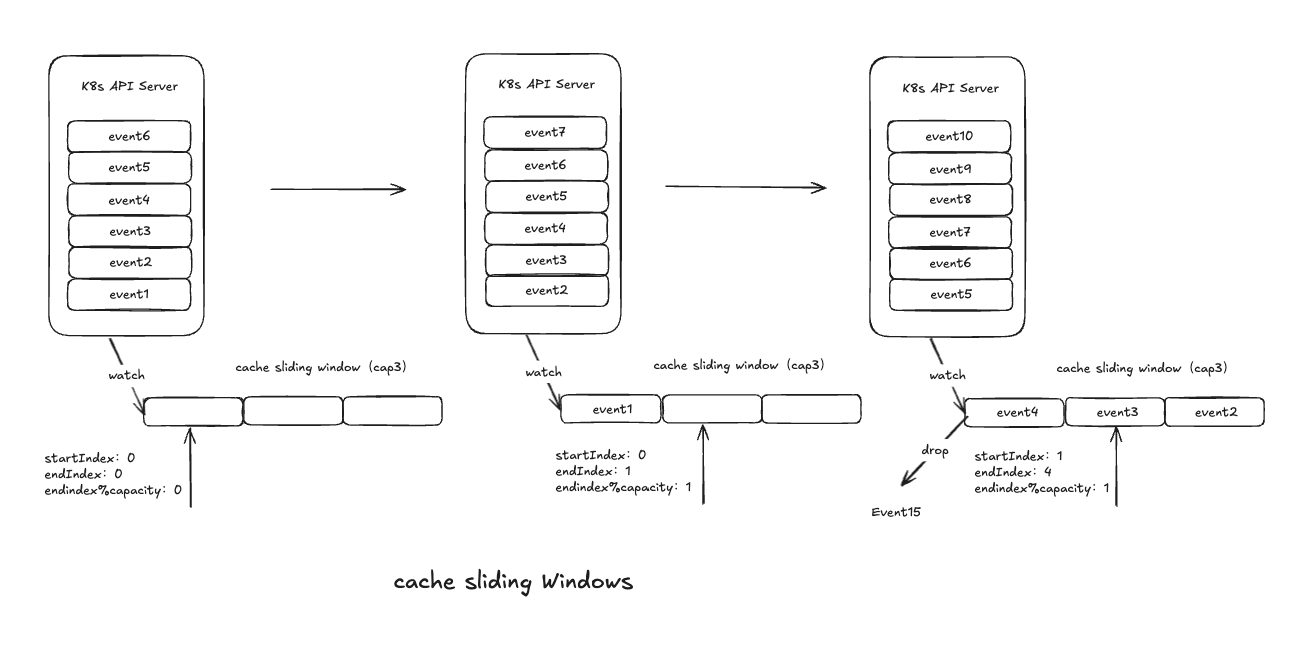
watchCache缓存滑动窗口
接收Reflector的事件回调,把事件分发到3个地方进行处理,其中之一就是缓存滑动窗口
常见缓存算法
- FIFO
- 特点:先进先出,实现简单
- 数据结构:队列
- 淘汰原则:当缓存满,移除最先进入到数据
- LRU
- 特点:按照时间维度,优先移除最久未使用
- 数据结构:链表和HashMap
- 淘汰原则:根据缓存使用时间维度,优先移除最不常用的缓存数据
- LFU
- 特点:按照统计维度,优先移除访问次数最少的数据
- 数据结构:链表和HashMap
- 淘汰原则:根据缓存数据使用次数,优先移除访问次数最少的缓存数据
watchCache实现
watchCache使用缓存滑动窗口,跟FIFO类似
-
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72// watchCache implements a Store interface.
// However, it depends on the elements implementing runtime.Object interface.
//
// watchCache is a "sliding window" (with a limited capacity) of objects
// observed from a watch.
type watchCache struct {
sync.RWMutex
// Condition on which lists are waiting for the fresh enough
// resource version.
cond *sync.Cond
// Maximum size of history window.
// 缓存滑动窗口大小,默认100
// 可以通过--default-watch-cache-size 参数设置
// 如果是0 禁用watchCache
capacity int
// upper bound of capacity since event cache has a dynamic size.
upperBoundCapacity int
// lower bound of capacity since event cache has a dynamic size.
lowerBoundCapacity int
// keyFunc is used to get a key in the underlying storage for a given object.
keyFunc func(runtime.Object) (string, error)
// getAttrsFunc is used to get labels and fields of an object.
getAttrsFunc func(runtime.Object) (labels.Set, fields.Set, error)
// cache is used a cyclic buffer - its first element (with the smallest
// resourceVersion) is defined by startIndex, its last element is defined
// by endIndex (if cache is full it will be startIndex + capacity).
// Both startIndex and endIndex can be greater than buffer capacity -
// you should always apply modulo capacity to get an index in cache array.
// 缓存滑动窗口,通过一个固定大小的数组形成一个环形缓冲区,可以向前滑动,当缓存滑动窗口满,移除最先进入到缓存滑动窗口的数据
cache []*watchCacheEvent
// 开始下标
startIndex int
// 结束下标
endIndex int
// store will effectively support LIST operation from the "end of cache
// history" i.e. from the moment just after the newest cached watched event.
// It is necessary to effectively allow clients to start watching at now.
// NOTE: We assume that <store> is thread-safe.
store cache.Indexer
// ResourceVersion up to which the watchCache is propagated.
resourceVersion uint64
// ResourceVersion of the last list result (populated via Replace() method).
listResourceVersion uint64
// This handler is run at the end of every successful Replace() method.
onReplace func()
// This handler is run at the end of every Add/Update/Delete method
// and additionally gets the previous value of the object.
eventHandler func(*watchCacheEvent)
// for testing timeouts.
clock clock.Clock
// An underlying storage.Versioner.
versioner storage.Versioner
// cacher's objectType.
objectType reflect.Type
// For testing cache interval invalidation.
indexValidator indexValidator
}
-
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10// Assumes that lock is already held for write.
func (w *watchCache) updateCache(event *watchCacheEvent) {
w.resizeCacheLocked(event.RecordTime)
if w.isCacheFullLocked() {
// Cache is full - remove the oldest element.
w.startIndex++
}
w.cache[w.endIndex%w.capacity] = event
w.endIndex++
}
Wacth的端点续传,确保资源不会丢失:
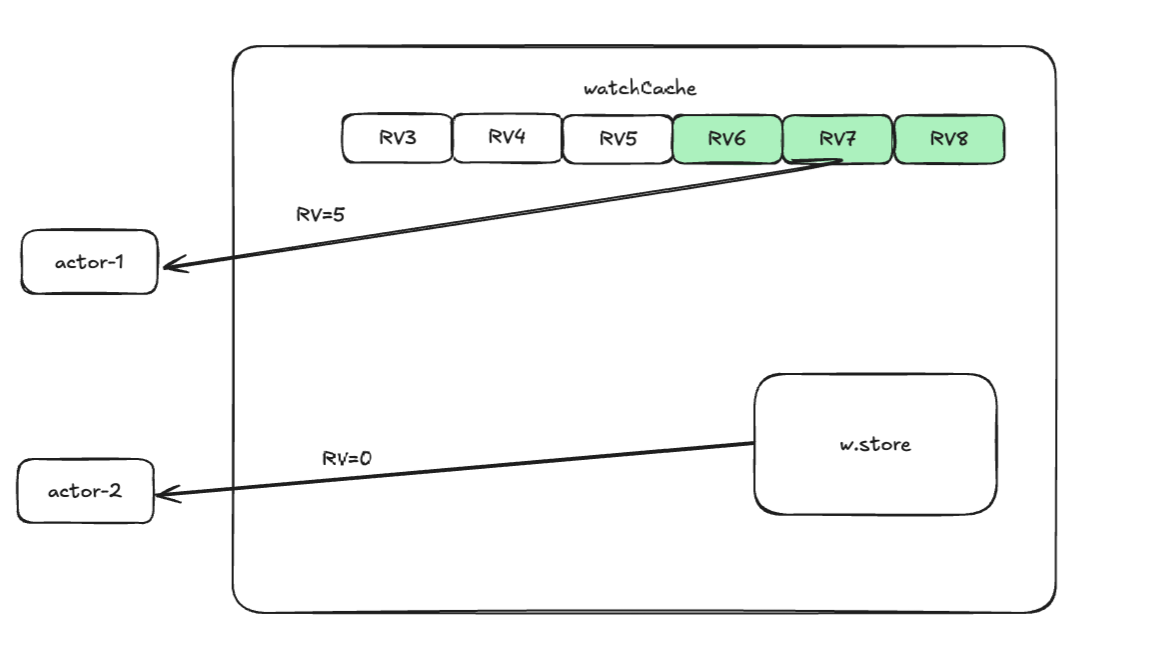
- actor1因为一些意外导致watch中断 中断前,最后一次是RV5
- 恢复时,请求Watch➕RV5
- watchCache从历史中,一次性把RV6、RV7、RV8一次性返回给actor1
- actor2使用RV0,全量获取cache历史记录
-
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50// getAllEventsSinceLocked returns a watchCacheInterval that can be used to
// retrieve events since a certain resourceVersion. This function assumes to
// be called under the watchCache lock.
func (w *watchCache) getAllEventsSinceLocked(resourceVersion uint64) (*watchCacheInterval, error) {
size := w.endIndex - w.startIndex
var oldest uint64
switch {
case w.listResourceVersion > 0 && w.startIndex == 0:
// If no event was removed from the buffer since last relist, the oldest watch
// event we can deliver is one greater than the resource version of the list.
oldest = w.listResourceVersion + 1
case size > 0:
// If the previous condition is not satisfied: either some event was already
// removed from the buffer or we've never completed a list (the latter can
// only happen in unit tests that populate the buffer without performing
// list/replace operations), the oldest watch event we can deliver is the first
// one in the buffer.
oldest = w.cache[w.startIndex%w.capacity].ResourceVersion
default:
return nil, fmt.Errorf("watch cache isn't correctly initialized")
}
if resourceVersion == 0 {
// resourceVersion = 0 means that we don't require any specific starting point
// and we would like to start watching from ~now.
// However, to keep backward compatibility, we additionally need to return the
// current state and only then start watching from that point.
//
// TODO: In v2 api, we should stop returning the current state - #13969.
ci, err := newCacheIntervalFromStore(w.resourceVersion, w.store, w.getAttrsFunc)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return ci, nil
}
if resourceVersion < oldest-1 {
return nil, errors.NewResourceExpired(fmt.Sprintf("too old resource version: %d (%d)", resourceVersion, oldest-1))
}
// Binary search the smallest index at which resourceVersion is greater than the given one.
f := func(i int) bool {
return w.cache[(w.startIndex+i)%w.capacity].ResourceVersion > resourceVersion
}
first := sort.Search(size, f)
indexerFunc := func(i int) *watchCacheEvent {
return w.cache[i%w.capacity]
}
ci := newCacheInterval(w.startIndex+first, w.endIndex, indexerFunc, w.indexValidator, &w.RWMutex)
return ci, nil
}
Underlying Storage底层存储对象
Underlying Storage是后端存储,真正和etcd交互的资源对象
-
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11// Create creates a storage backend based on given config.
func Create(c storagebackend.ConfigForResource, newFunc func() runtime.Object) (storage.Interface, DestroyFunc, error) {
switch c.Type {
case storagebackend.StorageTypeETCD2:
return nil, nil, fmt.Errorf("%s is no longer a supported storage backend", c.Type)
case storagebackend.StorageTypeUnset, storagebackend.StorageTypeETCD3:
return newETCD3Storage(c, newFunc)
default:
return nil, nil, fmt.Errorf("unknown storage type: %s", c.Type)
}
} 在默认情况下,资源对象(除了CustomReource)之外,在etcd中都使用二进制(application/vnd.kubernetes.protobbuf)编码存储
- 除了默认提供的Protobuf编码格式,还支持
application/json和application/yaml编码格式
- 除了默认提供的Protobuf编码格式,还支持
-
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31// Get implements storage.Interface.Get.
func (s *store) Get(ctx context.Context, key string, opts storage.GetOptions, out runtime.Object) error {
preparedKey, err := s.prepareKey(key)
if err != nil {
return err
}
startTime := time.Now()
getResp, err := s.client.KV.Get(ctx, preparedKey)
metrics.RecordEtcdRequestLatency("get", getTypeName(out), startTime)
if err != nil {
return err
}
if err = s.validateMinimumResourceVersion(opts.ResourceVersion, uint64(getResp.Header.Revision)); err != nil {
return err
}
if len(getResp.Kvs) == 0 {
if opts.IgnoreNotFound {
return runtime.SetZeroValue(out)
}
return storage.NewKeyNotFoundError(preparedKey, 0)
}
kv := getResp.Kvs[0]
data, _, err := s.transformer.TransformFromStorage(ctx, kv.Value, authenticatedDataString(preparedKey))
if err != nil {
return storage.NewInternalError(err.Error())
}
return decode(s.codec, s.versioner, data, out, kv.ModRevision)
}
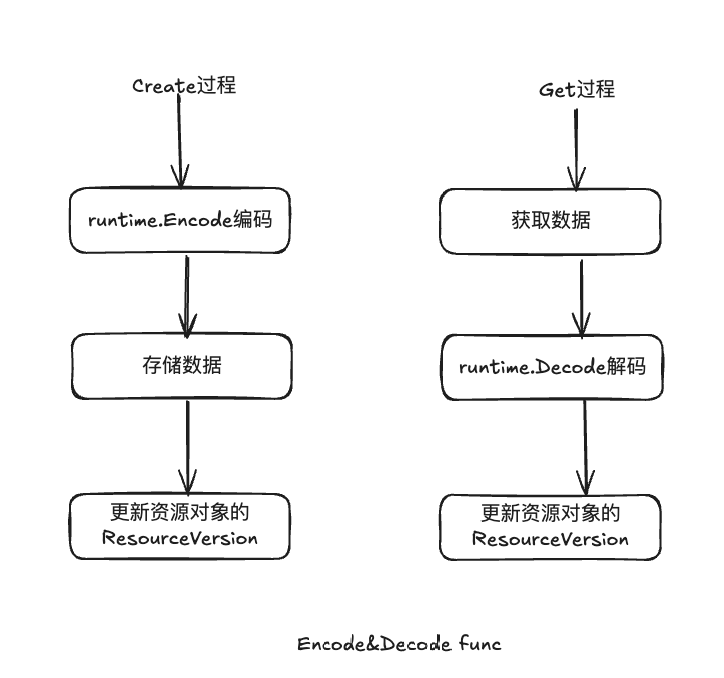
流程:
- 通过s.client.KV.Get func获取etcd集群中的资源对象的存储数据
- 通过protobufSerializer 编码器(code.Decode func)将二进制数据进行解码,将解码的数据存放到objptr中
- 通过version.UpdateObject func更新(填充资源对象)
K8s默认基于gRPC和etcd集群交互
Codec数据编码/解码
- 实例化Scheme资源
- 通过clientv3.New实例化etcd v3 client对象
- 通过newCode func实例化runtime.Codec
- 通过runtime.Decode解码器将资源对象解码为资源对象
- 通过runtime.Encode 转换为JSON打印
Strategy预处理
在K8s中,每种资源都有自己的预处理操作,它在资源对象的创建、更新、删除之前,实现资源持久化存储前的预处理。
一般都定义在
pkg/registry/<资源组>/<资源>/straregy.go中-
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9// GenericStore interface can be used for type assertions when we need to access the underlying strategies.
type GenericStore interface {
// 返回创建资源的预操作
GetCreateStrategy() rest.RESTCreateStrategy
// 返回资源更新的预操作
GetUpdateStrategy() rest.RESTUpdateStrategy
// 返回资源删除的预操作
GetDeleteStrategy() rest.RESTDeleteStrategy
}
Create Strategy预处理
-
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61// RESTCreateStrategy defines the minimum validation, accepted input, and
// name generation behavior to create an object that follows Kubernetes
// API conventions.
type RESTCreateStrategy interface {
// 获取和检查资源对象的APIVersion和Kind信息
runtime.ObjectTyper
// The name generator is used when the standard GenerateName field is set.
// The NameGenerator will be invoked prior to validation.
// 支持GenerateName,根据前缀自动生成名字
names.NameGenerator
// NamespaceScoped returns true if the object must be within a namespace.
// 判断当前资源是否在命名空间范围内
NamespaceScoped() bool
// PrepareForCreate is invoked on create before validation to normalize
// the object. For example: remove fields that are not to be persisted,
// sort order-insensitive list fields, etc. This should not remove fields
// whose presence would be considered a validation error.
//
// Often implemented as a type check and an initailization or clearing of
// status. Clear the status because status changes are internal. External
// callers of an api (users) should not be setting an initial status on
// newly created objects.
// 定义创建资源对象前的操作
PrepareForCreate(ctx context.Context, obj runtime.Object)
// Validate returns an ErrorList with validation errors or nil. Validate
// is invoked after default fields in the object have been filled in
// before the object is persisted. This method should not mutate the
// object.
// 验证对象是否合法
Validate(ctx context.Context, obj runtime.Object) field.ErrorList
// WarningsOnCreate returns warnings to the client performing a create.
// WarningsOnCreate is invoked after default fields in the object have been filled in
// and after Validate has passed, before Canonicalize is called, and the object is persisted.
// This method must not mutate the object.
//
// Be brief; limit warnings to 120 characters if possible.
// Don't include a "Warning:" prefix in the message (that is added by clients on output).
// Warnings returned about a specific field should be formatted as "path.to.field: message".
// For example: `spec.imagePullSecrets[0].name: invalid empty name ""`
//
// Use warning messages to describe problems the client making the API request should correct or be aware of.
// For example:
// - use of deprecated fields/labels/annotations that will stop working in a future release
// - use of obsolete fields/labels/annotations that are non-functional
// - malformed or invalid specifications that prevent successful handling of the submitted object,
// but are not rejected by validation for compatibility reasons
//
// Warnings should not be returned for fields which cannot be resolved by the caller.
// For example, do not warn about spec fields in a subresource creation request.
// 定义在创建资源对象的警告信息
WarningsOnCreate(ctx context.Context, obj runtime.Object) []string
// Canonicalize allows an object to be mutated into a canonical form. This
// ensures that code that operates on these objects can rely on the common
// form for things like comparison. Canonicalize is invoked after
// validation has succeeded but before the object has been persisted.
// This method may mutate the object. Often implemented as a type check or
// empty method.
// 在创建资源前,进行规范化处理,确保存储的数据格式是否通用
Canonicalize(obj runtime.Object)
}
Update Strategy预处理
-
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51// RESTUpdateStrategy defines the minimum validation, accepted input, and
// name generation behavior to update an object that follows Kubernetes
// API conventions. A resource may have many UpdateStrategies, depending on
// the call pattern in use.
type RESTUpdateStrategy interface {
runtime.ObjectTyper
// NamespaceScoped returns true if the object must be within a namespace.
NamespaceScoped() bool
// AllowCreateOnUpdate returns true if the object can be created by a PUT.
// 判断当前资源是否在命名空间范围内
AllowCreateOnUpdate() bool
// PrepareForUpdate is invoked on update before validation to normalize
// the object. For example: remove fields that are not to be persisted,
// sort order-insensitive list fields, etc. This should not remove fields
// whose presence would be considered a validation error.
PrepareForUpdate(ctx context.Context, obj, old runtime.Object)
// ValidateUpdate is invoked after default fields in the object have been
// filled in before the object is persisted. This method should not mutate
// the object.
ValidateUpdate(ctx context.Context, obj, old runtime.Object) field.ErrorList
// WarningsOnUpdate returns warnings to the client performing the update.
// WarningsOnUpdate is invoked after default fields in the object have been filled in
// and after ValidateUpdate has passed, before Canonicalize is called, and before the object is persisted.
// This method must not mutate either object.
//
// Be brief; limit warnings to 120 characters if possible.
// Don't include a "Warning:" prefix in the message (that is added by clients on output).
// Warnings returned about a specific field should be formatted as "path.to.field: message".
// For example: `spec.imagePullSecrets[0].name: invalid empty name ""`
//
// Use warning messages to describe problems the client making the API request should correct or be aware of.
// For example:
// - use of deprecated fields/labels/annotations that will stop working in a future release
// - use of obsolete fields/labels/annotations that are non-functional
// - malformed or invalid specifications that prevent successful handling of the submitted object,
// but are not rejected by validation for compatibility reasons
//
// Warnings should not be returned for fields which cannot be resolved by the caller.
// For example, do not warn about spec fields in a status update.
WarningsOnUpdate(ctx context.Context, obj, old runtime.Object) []string
// Canonicalize allows an object to be mutated into a canonical form. This
// ensures that code that operates on these objects can rely on the common
// form for things like comparison. Canonicalize is invoked after
// validation has succeeded but before the object has been persisted.
// This method may mutate the object.
Canonicalize(obj runtime.Object)
// AllowUnconditionalUpdate returns true if the object can be updated
// unconditionally (irrespective of the latest resource version), when
// there is no resource version specified in the object.
AllowUnconditionalUpdate() bool
}
Delete Strategy预处理
-
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97// BeforeDelete tests whether the object can be gracefully deleted.
// If graceful is set, the object should be gracefully deleted. If gracefulPending
// is set, the object has already been gracefully deleted (and the provided grace
// period is longer than the time to deletion). An error is returned if the
// condition cannot be checked or the gracePeriodSeconds is invalid. The options
// argument may be updated with default values if graceful is true. Second place
// where we set deletionTimestamp is pkg/registry/generic/registry/store.go.
// This function is responsible for setting deletionTimestamp during gracefulDeletion,
// other one for cascading deletions.
func BeforeDelete(strategy RESTDeleteStrategy, ctx context.Context, obj runtime.Object, options *metav1.DeleteOptions) (graceful, gracefulPending bool, err error) {
objectMeta, gvk, kerr := objectMetaAndKind(strategy, obj)
if kerr != nil {
return false, false, kerr
}
if errs := validation.ValidateDeleteOptions(options); len(errs) > 0 {
return false, false, errors.NewInvalid(schema.GroupKind{Group: metav1.GroupName, Kind: "DeleteOptions"}, "", errs)
}
// Checking the Preconditions here to fail early. They'll be enforced later on when we actually do the deletion, too.
if options.Preconditions != nil {
if options.Preconditions.UID != nil && *options.Preconditions.UID != objectMeta.GetUID() {
return false, false, errors.NewConflict(schema.GroupResource{Group: gvk.Group, Resource: gvk.Kind}, objectMeta.GetName(), fmt.Errorf("the UID in the precondition (%s) does not match the UID in record (%s). The object might have been deleted and then recreated", *options.Preconditions.UID, objectMeta.GetUID()))
}
if options.Preconditions.ResourceVersion != nil && *options.Preconditions.ResourceVersion != objectMeta.GetResourceVersion() {
return false, false, errors.NewConflict(schema.GroupResource{Group: gvk.Group, Resource: gvk.Kind}, objectMeta.GetName(), fmt.Errorf("the ResourceVersion in the precondition (%s) does not match the ResourceVersion in record (%s). The object might have been modified", *options.Preconditions.ResourceVersion, objectMeta.GetResourceVersion()))
}
}
// Negative values will be treated as the value `1s` on the delete path.
if gracePeriodSeconds := options.GracePeriodSeconds; gracePeriodSeconds != nil && *gracePeriodSeconds < 0 {
options.GracePeriodSeconds = utilpointer.Int64(1)
}
if deletionGracePeriodSeconds := objectMeta.GetDeletionGracePeriodSeconds(); deletionGracePeriodSeconds != nil && *deletionGracePeriodSeconds < 0 {
objectMeta.SetDeletionGracePeriodSeconds(utilpointer.Int64(1))
}
gracefulStrategy, ok := strategy.(RESTGracefulDeleteStrategy)
if !ok {
// If we're not deleting gracefully there's no point in updating Generation, as we won't update
// the obcject before deleting it.
return false, false, nil
}
// if the object is already being deleted, no need to update generation.
if objectMeta.GetDeletionTimestamp() != nil {
// if we are already being deleted, we may only shorten the deletion grace period
// this means the object was gracefully deleted previously but deletionGracePeriodSeconds was not set,
// so we force deletion immediately
// IMPORTANT:
// The deletion operation happens in two phases.
// 1. Update to set DeletionGracePeriodSeconds and DeletionTimestamp
// 2. Delete the object from storage.
// If the update succeeds, but the delete fails (network error, internal storage error, etc.),
// a resource was previously left in a state that was non-recoverable. We
// check if the existing stored resource has a grace period as 0 and if so
// attempt to delete immediately in order to recover from this scenario.
if objectMeta.GetDeletionGracePeriodSeconds() == nil || *objectMeta.GetDeletionGracePeriodSeconds() == 0 {
return false, false, nil
}
// only a shorter grace period may be provided by a user
if options.GracePeriodSeconds != nil {
period := int64(*options.GracePeriodSeconds)
if period >= *objectMeta.GetDeletionGracePeriodSeconds() {
return false, true, nil
}
newDeletionTimestamp := metav1.NewTime(
objectMeta.GetDeletionTimestamp().Add(-time.Second * time.Duration(*objectMeta.GetDeletionGracePeriodSeconds())).
Add(time.Second * time.Duration(*options.GracePeriodSeconds)))
objectMeta.SetDeletionTimestamp(&newDeletionTimestamp)
objectMeta.SetDeletionGracePeriodSeconds(&period)
return true, false, nil
}
// graceful deletion is pending, do nothing
options.GracePeriodSeconds = objectMeta.GetDeletionGracePeriodSeconds()
return false, true, nil
}
// `CheckGracefulDelete` will be implemented by specific strategy
if !gracefulStrategy.CheckGracefulDelete(ctx, obj, options) {
return false, false, nil
}
if options.GracePeriodSeconds == nil {
return false, false, errors.NewInternalError(fmt.Errorf("options.GracePeriodSeconds should not be nil"))
}
now := metav1.NewTime(metav1.Now().Add(time.Second * time.Duration(*options.GracePeriodSeconds)))
objectMeta.SetDeletionTimestamp(&now)
objectMeta.SetDeletionGracePeriodSeconds(options.GracePeriodSeconds)
// If it's the first graceful deletion we are going to set the DeletionTimestamp to non-nil.
// Controllers of the object that's being deleted shouldn't take any nontrivial actions, hence its behavior changes.
// Thus we need to bump object's Generation (if set). This handles generation bump during graceful deletion.
// The bump for objects that don't support graceful deletion is handled in pkg/registry/generic/registry/store.go.
if objectMeta.GetGeneration() > 0 {
objectMeta.SetGeneration(objectMeta.GetGeneration() + 1)
}
return true, false, nil
}


